Home >
News > Bioinspired Metal–Organic Framework for Trace CO₂ Capture
Bioinspired Metal–Organic Framework for Trace CO₂ Capture
Summary:
Researchers from The Ohio State University developed a bio-inspired Zn–OH-functionalized metal–organic framework (MOF) that captures trace CO₂ from air at 400 ppm with 2.2 mmol g⁻¹ capacity and mild 100 °C regeneration.
Background:
1. Trace CO₂ removal is essential for closed habitats, yet liquid amine scrubbing is energy-intensive and amine-grafted solids degrade during thermal cycling.
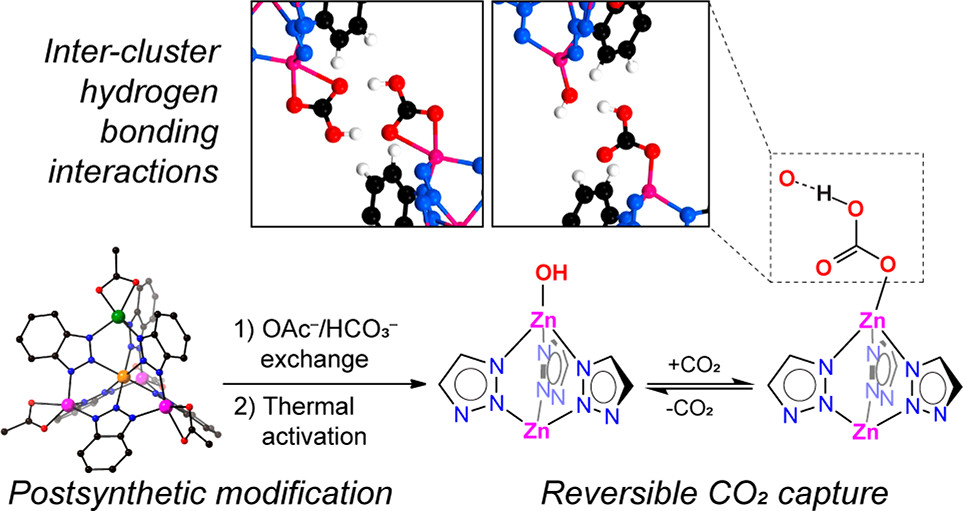
2. The team mimicked α-carbonic-anhydrase active sites, introducing nucleophilic Zn–OH pairs into a benzotriazolate MOF via gentle acetate/bicarbonate ligand exchange.
Research Content:
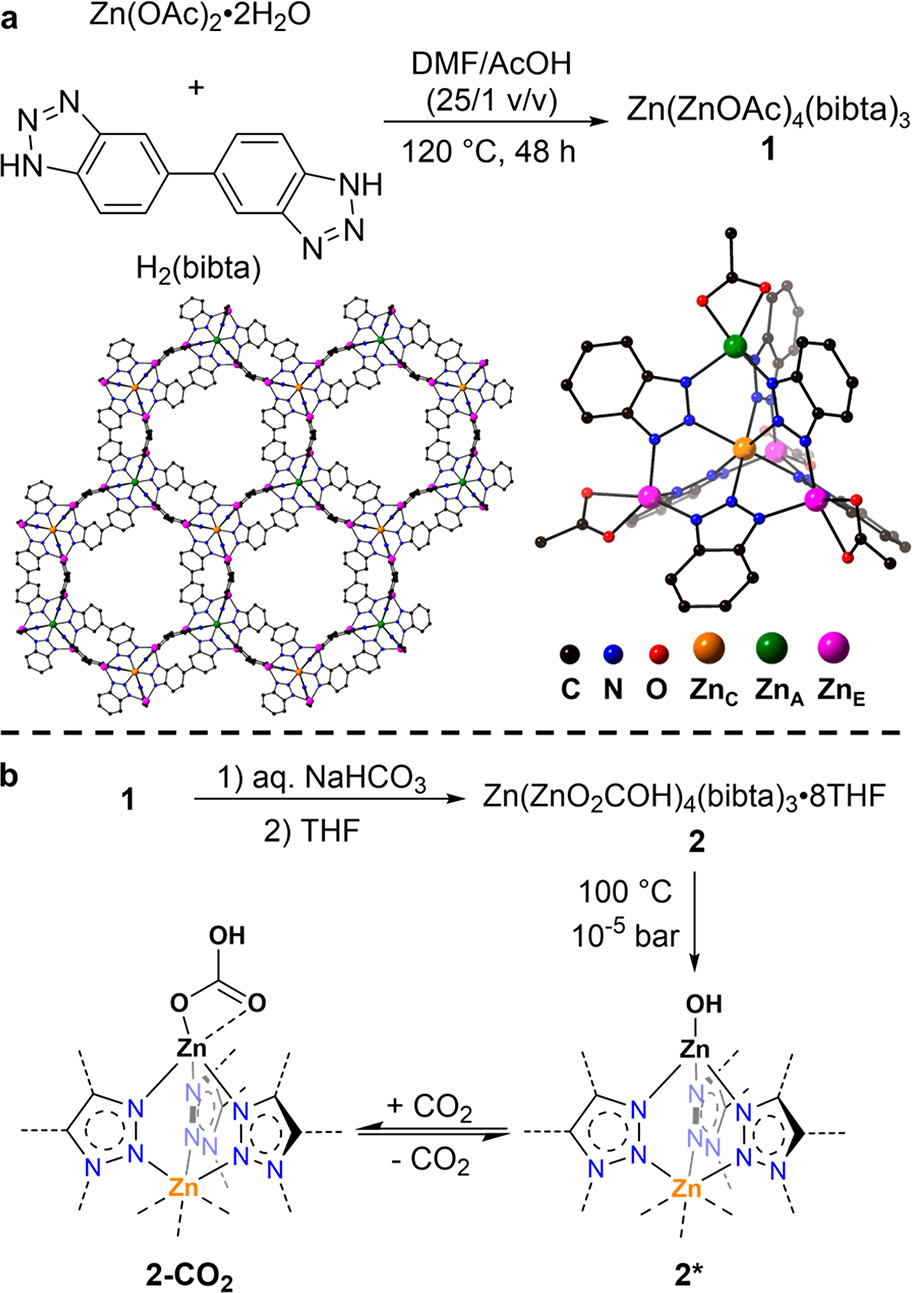
1. Synthesis: CFA-1 (Zn₅(OAc)₄(bibta)₃) was soaked in 0.1 M NaHCO₃ (pH 8) and activated at 100 °C to yield Zn–OH sites (2*).
2. Characterizations:
– BET: 2* 2522 m² g⁻¹ (vs 2075 m² g⁻¹ for parent).
– PXRD retains crystallinity; TGA stable to 400 °C.
– DRIFTS shows Zn–O₂COH (1340, 1585 cm⁻¹) and H-bonded O–H (2657 cm⁻¹).
3. Application: 5.8 wt % uptake from 395 ppm CO₂/air; 100 °C thermal-swing cycles lose <5 % capacity after 10 runs.
4. Mechanism: DFT reveals cooperative inter-cluster H-bonding boosts CO₂ binding from –37.5 kJ mol⁻¹ (isolated) to –71 kJ mol⁻¹ (paired Zn–OH), enabling reversible Zn–OH/Zn–O₂COH chemisorption.
Outlook:
The study delivers a low-temperature regenerable, amine-free MOF sorbent for direct-air-capture, demonstrating that bio-inspired secondary-sphere engineering can enhance trace-gum adsorption performance.
Bioinspired Metal–Organic Framework for Trace CO₂ Capture
Authors: Caitlin E. Bien, Kai K. Chen, Szu-Chia Chien, Benjamin R. Reiner, Li-Chiang Lin, Casey R. Wade*, W. S. Winston Ho
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b06109
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.8b06109
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

