Steam, CO₂/H₂O in CALF-20
Summary:
The authors from Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of South Alabama and Department of Chemistry, University of Calgary developed CALF-20 (a steam-stable metal-organic framework with selective CO₂ physisorption), achieving insights into its CO₂/H₂O adsorption thermodynamics and diffusion kinetics for industrial CO₂ capture application.
Background:
1. To address CO₂ emission (65% of anthropogenic greenhouse gases) and limitations of liquid amine CO₂ capture (corrosion, high cost), previous researchers studied solid adsorbents like MOFs. However, flue gas water vapor’s impact on CO₂ adsorption was rarely reported, and CALF-20’s CO₂/H₂O diffusion rates and high-temperature water adsorption data were lacking.
2. The authors in this work proposed measuring CALF-20’s CO₂/H₂O single-component diffusion rates via concentration swing frequency response (CSFR) and high-temperature (25-175℃) water adsorption isotherms, obtaining key parameters for industrial CO₂ capture system modeling.
Research Content:
1.Synthesis: The authors synthesized CALF-20 by adding zinc oxalate, 1,2,4-triazole, and methanol into a 125 mL Teflon autoclave, heating to 180℃ for 48 h, then washing with methanol and air-drying.
2.Characterizations:
1) BET surface area: 666 m²/g (consistent with literature 528 m²/g); no pore size distribution data provided.
2) No SEM/TEM tests mentioned.
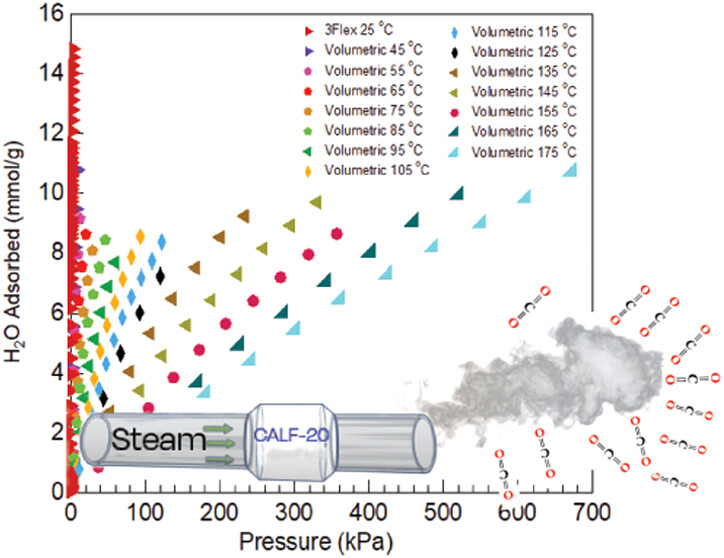
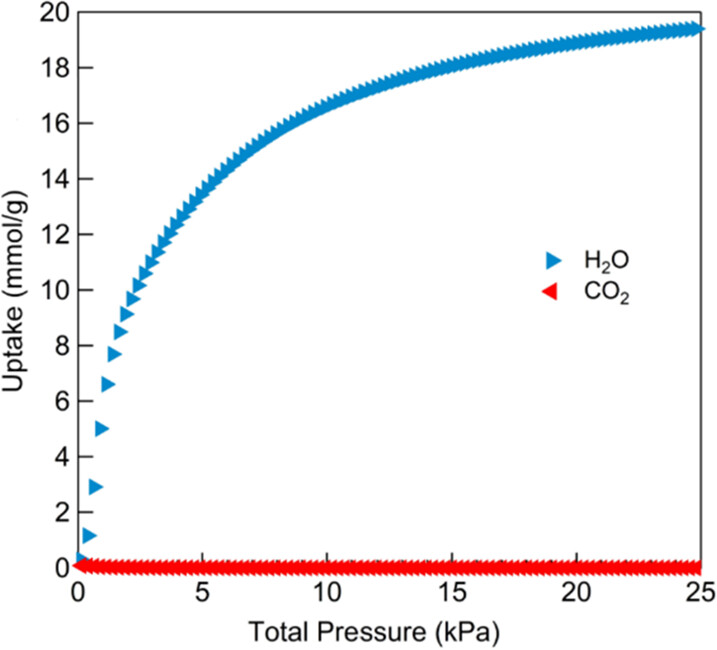
3) Adsorption isotherms: 25℃ CO₂/H₂O single-component isotherms (CO₂ physisorption, H₂O S-shaped adsorption); 25-175℃ water isotherms (water capacity changes slightly above 45℃); isosteric heat of water adsorption: average 48 kJ/mol.
3.Application: Tested in CO₂ capture from humid flue gas. Results: CALF-20 retains CO₂ capacity (2%-14% CO₂, wide humidity); H₂O diffusion rate similar to MOF-333/BPL activated carbon; α-to-β phase transition has little effect on CO₂ adsorption.
4.Mechanism: H₂O adsorption’s S-shape relates to α-to-β phase transition (ligand reorientation); CO₂ physisorption is due to weak interaction between CO₂ oxygen and triazole hydrogen; water diffusion follows micropore model, CO₂ diffusion follows linear driving force model.
Outlook:
This research clarifies CALF-20’s CO₂/H₂O adsorption and diffusion behaviors, provides key data for industrial CO₂ capture system design, and promotes MOFs’ application in humid flue gas CO₂ capture.
Steam Isotherms, CO₂/H₂O Mixed-Gas Isotherms, and Single Component CO₂ and H₂O Diffusion Rates in CALF-20
Authors: Jon Hastings, Thomas Lassitter, Nicholas Fylstra, George K. H. Shimizu, T. Grant Glover*
DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.4c00373
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.iecr.4c00373
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

