Home >
News > Rapid synthesis of CALF-20 under ambient conditions
Rapid synthesis of CALF-20 under ambient conditions
Summary:
The authors from Kansai University (Japan) and Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation (Japan): developed CALF-20 (a zinc-based MOF) with rapid crystallization, high CO₂ adsorption capacity, and high yield, achieving efficient CO₂ capture in gas adsorption field.
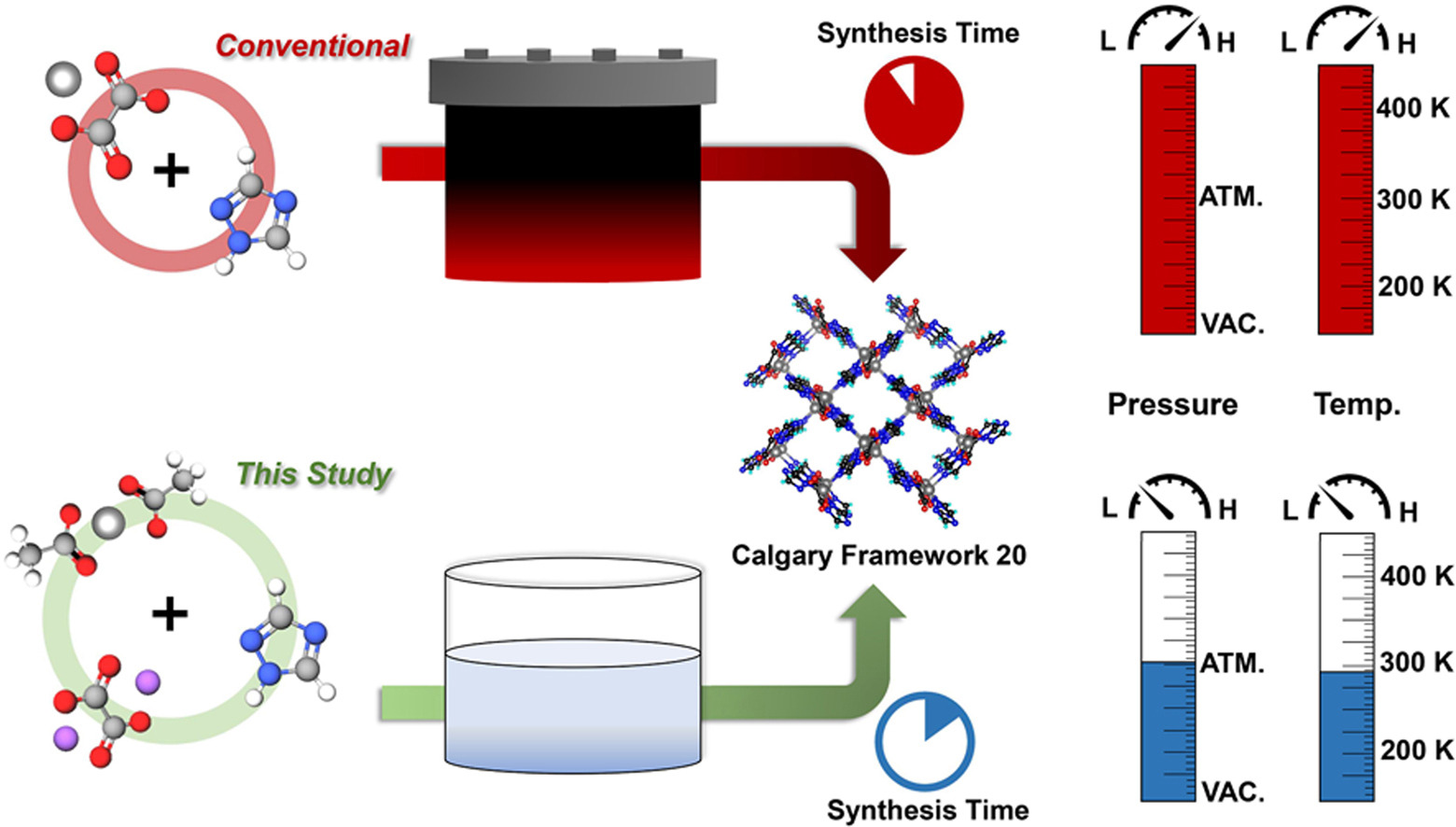
Background:
1. To address the high energy consumption and long reaction time of traditional solvothermal synthesis of CALF-20 (180℃, 48 h), previous researchers used pure alcohol solvents but still relied on high-temperature/pressure conditions, failing to reduce energy and time costs.
2. The authors proposed an innovative synthesis method in H₂O/methanol solution under room temperature (298 K) and normal pressure (101.3 kPa), realizing CALF-20 crystallization in 6 min with 93.3% yield and excellent CO₂ adsorption performance.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized CALF-20 via a three-step stirring method: first, dissolve Zn(OAc)₂·2H₂O in H₂O/methanol (optimal ratio 16:4, vol) and stir 5 min; second, add sodium oxalate, stir 5 min to form a suspension; third, add 1,2,4-triazole, stir 6-120 min, then centrifuge, wash with H₂O, and dry/activate.
2. Characterizations:
1) BET: Optimal product has BET surface area 520 m²/g, micropore volume 0.19 cm³/g (t-plot method), N₂ adsorption isotherm (77 K) shows typical microporous (Type I) feature.
2) SEM tests show: No CALF-20 particles at 5 min aging; angular CALF-20 particles form at 6 min; raw material addition order slightly affects particle size (no specific size data).
3) Other tests: PXRD confirms pure CALF-20 phase at 16:4 solvent ratio; ICP shows Na⁺ removed completely after washing; TGA reveals two-step weight loss (dehydration, framework decomposition); FTIR verifies functional groups of CALF-20.
3. Application:
The material was tested for CO₂ adsorption (298 K, 100 kPa): optimal product has CO₂ uptake 3.84 mmol/g, comparable to solvothermal-synthesized CALF-20; adsorption performance correlates with BET surface area/micropore volume.
4. Mechanism:
- Experiment result analysis: H₂O promotes dissolution of raw materials and deprotonation of 1,2,4-triazole; methanol adjusts coordination environment of Zn²⁺; washing removes unreacted substances to ensure pore accessibility.
- Performance mechanism: Acetate anion (from Zn(OAc)₂) induces deprotonation of 1,2,4-triazole, facilitating formation of Zn-oxalate-1,2,4-triazole 3D network (micropores for CO₂ adsorption).
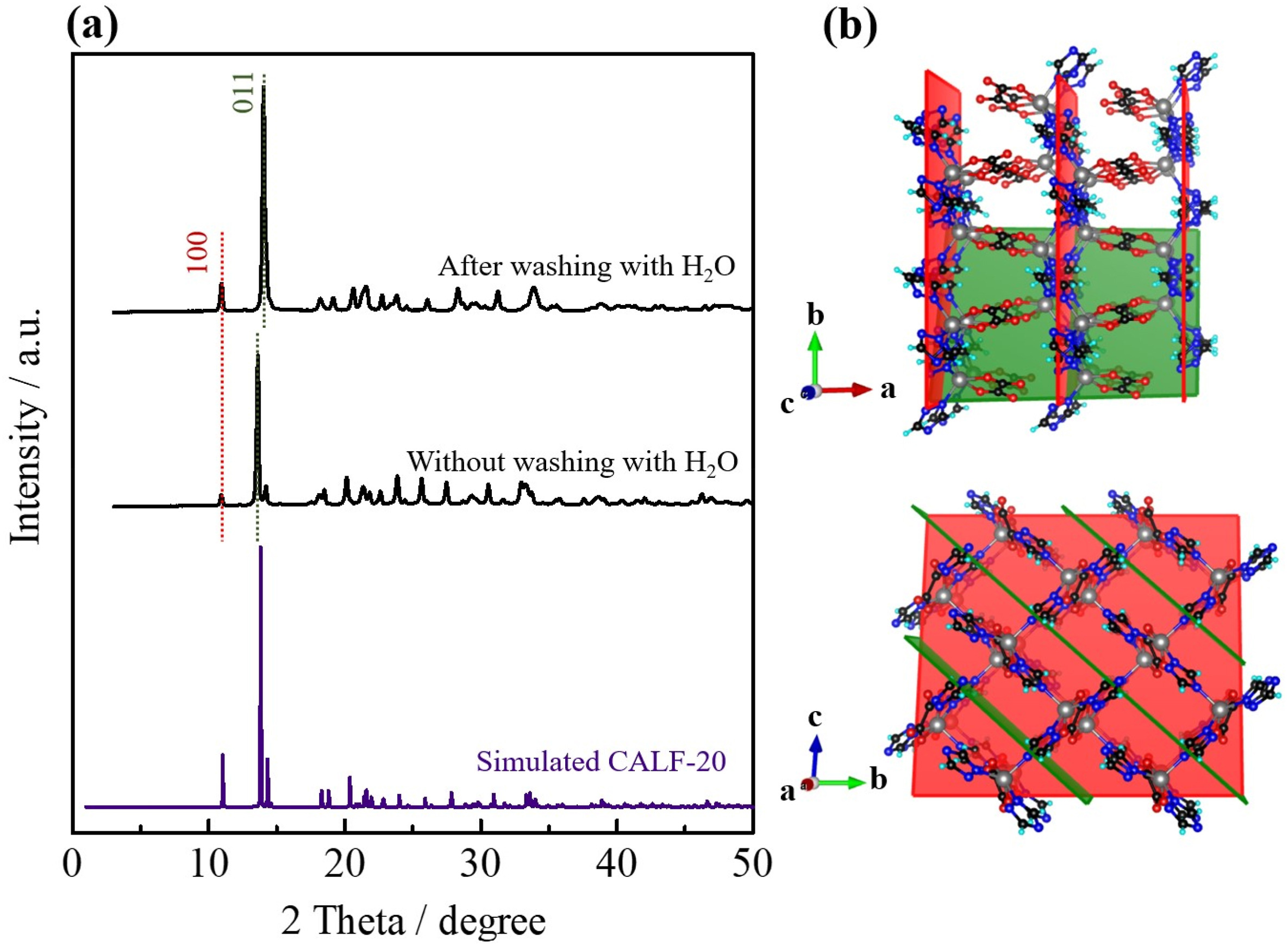
Outlook:
This research realizes rapid, low-energy synthesis of CALF-20, solves the high energy/time cost of traditional methods, and provides a feasible scheme for industrial production of CALF-20 and efficient CO₂ capture.
Rapid synthesis of metal-organic framework CALF-20 in H₂O/methanol solution under room temperature and normal pressure
Authors: Yuto Higuchi, Miki Sugita, Saki Moriya, Takahiko Takewaki, Shunsuke Tanaka
DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2024.113137
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1387181124001598
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

