Home >
News > Mechanochemically synthesized CALF-20 for TSA CO₂ capture
Mechanochemically synthesized CALF-20 for TSA CO₂ capture
Summary:
The authors (Federica Raganati et al., affiliations not specified in documents) developed CALF-20 (a zinc-based MOF) with high CO₂ adsorption capacity, good cyclic stability, and microporous structure, achieving efficient CO₂ capture in temperature swing adsorption (TSA) field.
Background:
1. To address global CO₂ emission and climate change issues, previous researchers focused on post-combustion CO₂ capture via adsorption, using MOFs (with high surface area/tunable pores) as adsorbents. However, traditional MOF synthesis (e.g., solvothermal) had high solvent usage, long reaction time, and high energy consumption.
2. The authors proposed an innovative reduced-solvent mechanochemical synthesis method for CALF-20, shortening reaction time, reducing solvent/energy use, and obtaining CALF-20 with excellent TSA CO₂ capture performance.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized CALF-20 using solvent-assisted mechanical milling (with stainless-steel vial, Zirconia balls) with zinc oxalate and 1,2,4-triazole as precursors, methanol as additive (η=0.90 μl mg⁻¹), milling for 30 min (CALF20BM05H) or 1 h (CALF20BM1H), followed by water washing, centrifugation (10000 rpm, 10 min), drying (70℃ overnight), and activation (180℃, 3 h).
2. Characterizations:
1) BET: CALF20BM05H and CALF20BM1H had BET specific surface areas of 338±10 m²g⁻¹ and 350±15 m²g⁻¹, respectively; nitrogen adsorption isotherm (77K) showed microporous (type 1) feature with slight mesoporous volume.
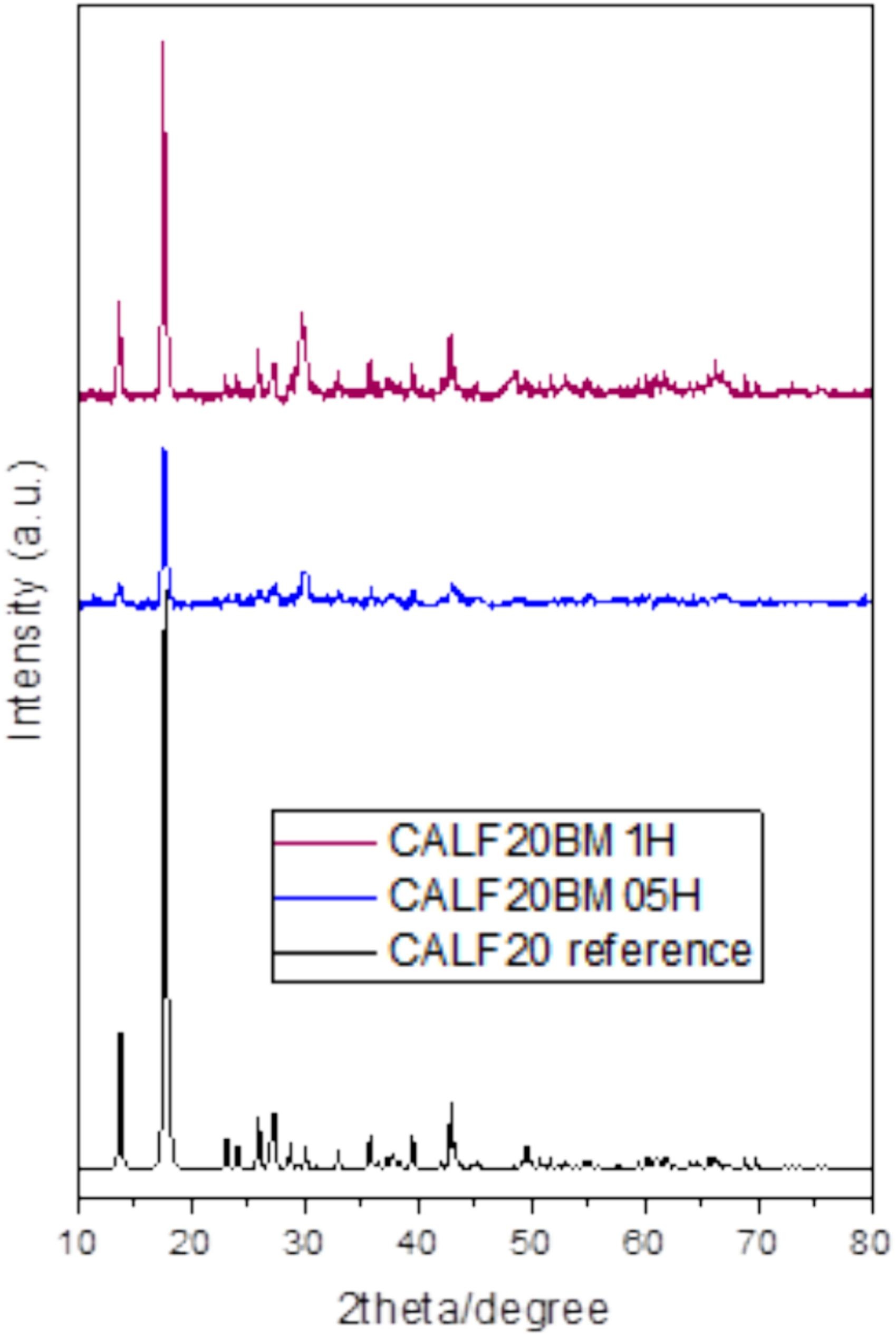
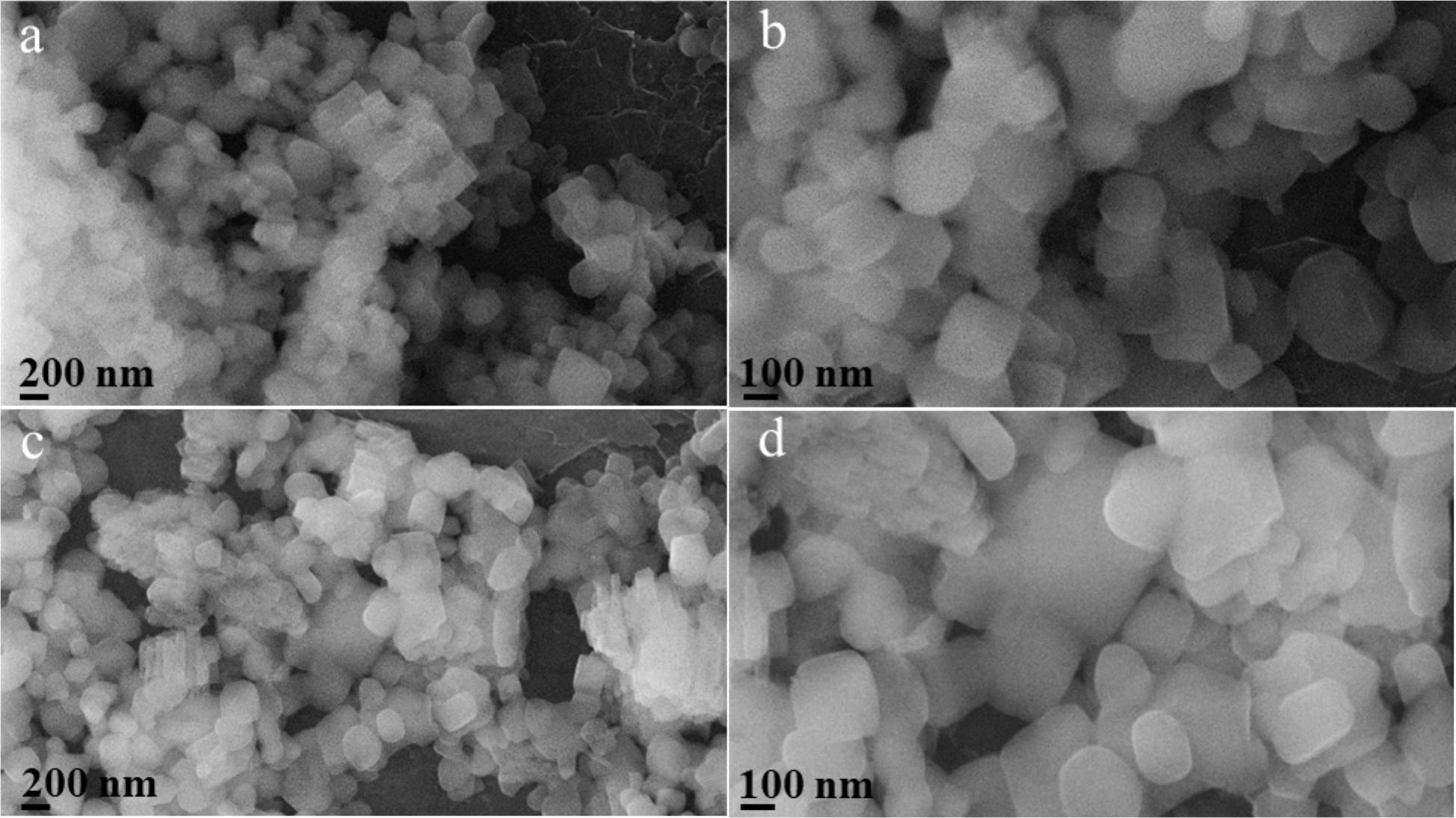
2) SEM tests show CALF20BM05H had 100-200 nm agglomerated crystals; CALF20BM1H had larger crystals. XRD showed crystallite sizes of 65±2 nm (30 min milling) and 171±4 nm (1 h milling).
3) No electrochemical/optical tests mentioned; thermodynamic analysis (Sips isotherm: R²>0.99, 28℃ qₘ=4.065 mmol/g; Qst=22-29 kJ/mol) and kinetic analysis (pseudo-first-order model: R²>0.999, Ea=15.5 kJ/mol) were conducted.
3. Application:
The material was tested in fixed-bed reactor for TSA CO₂ capture:
- Adsorption (28-130℃, CO₂ partial pressure 0.03-0.2 atm): max adsorption capacity 2.55 mmol/g (28℃, 0.2 atm CO₂).
- Desorption (40-150℃, N₂ purge): 150℃ achieved ~100% recovery in <1 min; 10 cycles showed stable qe, tb, Δτ, ψ.
4. Mechanism:
- Thermodynamic analysis: Qst=22-29 kJ/mol <80 kJ/mol, confirming physisorption; Sips model n>1 indicated surface heterogeneity.
- Kinetic analysis: pseudo-first-order model fit best, consistent with physisorption (weak van der Waals interactions); Ea=15.5 kJ/mol supported low-energy physical adsorption.
Outlook:
This research realized green synthesis of CALF-20 via mechanochemistry, confirmed its high/stable CO₂ capture performance in TSA, providing a sustainable adsorbent and theoretical basis for post-combustion CO₂ capture industrialization.
CALF-20 obtained by mechanochemical synthesis for temperature swing adsorption CO₂ Capture: A thermodynamic and kinetic study
Authors: Federica Raganati, Mariangela Bellusci, Francesco Leardi, Francesca Varsano, Paola Ammendola
DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.159966
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S138589472500765X
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

