Home >
News > Synergy Effect of Pore Structure and Amount of Carboxyl Site for Effective Removal of Pb²⁺ in Metal−Organic Frameworks
Synergy Effect of Pore Structure and Amount of Carboxyl Site for Effective Removal of Pb²⁺ in Metal−Organic Frameworks
Summary:
The authors from Taiyuan University of Science and Technology and Tianjin Polytechnic University developed carboxyl-grafted metal-organic frameworks (UiO-66-(COOH)ₙ, n=0,1,2,4) with tunable carboxyl content and pore structure, achieving high Pb²⁺ adsorption capacity (up to 420.2 mg/g) and 99.99% removal rate in the application of aqueous Pb²⁺ removal.
Background:
1. To address the problem of toxic Pb²⁺ pollution (harmful to human systems) and deficiencies of existing adsorbents (low capacity, slow rate, poor regeneration), previous researchers used membrane filtration, precipitation, and adsorbents like MOFs (e.g., TMU-5, MOF-545), yet most had limited performance.
2. The authors proposed synthesizing UiO-66-(COOH)ₙ with controllable carboxyl groups, exploring the synergy of carboxyl sites and pore structure, and obtained excellent Pb²⁺ adsorption and regeneration performance.
Research Content:
1.Synthesis: The authors synthesized UiO-66 and UiO-66-COOH via reported methods; UiO-66-(COOH)₂ and UiO-66-(COOH)₄ were synthesized with modifications (refluxing in 373K water and 343K methanol for 24h each to remove impurities).
2.Characterizations:
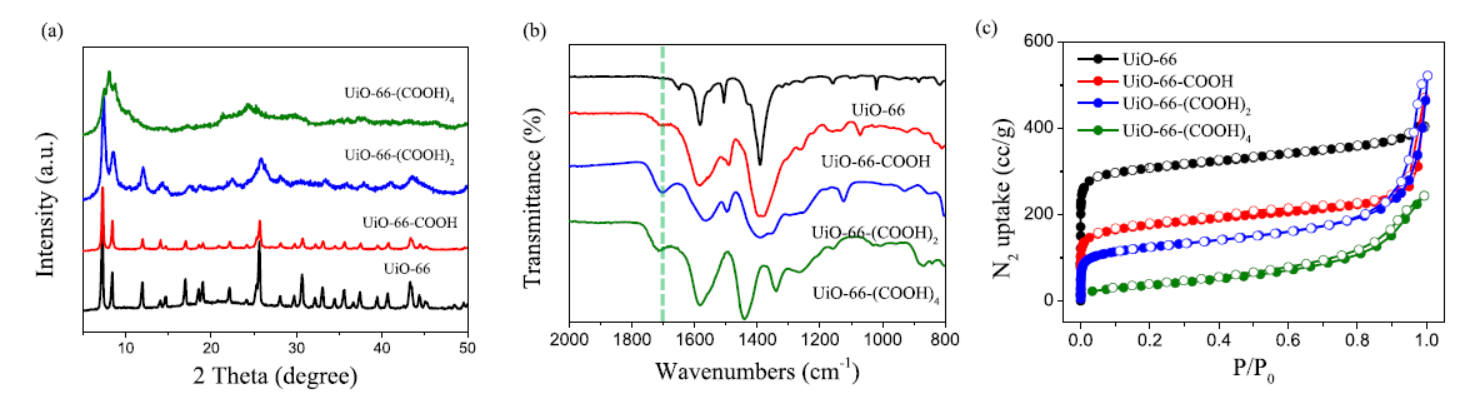
1) BET results: UiO-66 (1198 m²/g, 0.62 cm³/g), UiO-66-COOH (645 m²/g, 0.43 cm³/g), UiO-66-(COOH)₂ (443 m²/g, 0.22 cm³/g), UiO-66-(COOH)₄ (135 m²/g, 0.23 cm³/g); carboxyl increase reduced BET and pore volume.
2) SEM/EDS mapping: Pb²⁺ adsorption was most obvious on UiO-66-(COOH)₂; Zr/Pb ratios from adsorption and EDS were consistent (e.g., 1:0.642 vs 1:0.699 for UiO-66-(COOH)₂).
3) Other tests: PXRD showed UiO-66-(COOH)ₙ had similar topology; FT-IR revealed ~1720 cm⁻¹ peaks (uncoordinated carboxyl); XPS showed Pb-O bond (530.8 eV) and shifted Pb 4f peaks.
3.Application: In Pb²⁺ adsorption, UiO-66-(COOH)₂ had 420.2 mg/g capacity (superior to others), 99.99% removal (<100 ppm, 0.5 mg/mL dosage), and retained 85% capacity after 4 regenerations.
4.Mechanism: FT-IR showed carboxyl participation; XPS and DFT (BE=-284 kJ/mol, Pb-O distance=2.428 Å) confirmed strong Pb²⁺-carboxyl interaction; UiO-66-(COOH)₂’s synergy of carboxyl content and pore structure optimized adsorption.
Outlook:
This research develops high-performance UiO-66-(COOH)₂ for Pb²⁺ removal, clarifies the synergy of carboxyl and pore structure, and provides guidance for designing efficient heavy metal adsorbents.
Synergy Effect of Pore Structure and Amount of Carboxyl Site for Effective Removal of Pb²⁺ in Metal−Organic Frameworks
Authors: Xudong Zhao, Yaxin Wang, Yali Li, Wenjuan Xue, Jian Li, Huiyuan Wu, Yuezhong Zhang, Bingzheng Li, Wen Liu, Zhuqing Gao, Hongliang Huang
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jced.9b00130
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00130
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

