Home >
News > Tuning the Adsorption Properties of UiO-66 via Ligand Functionalization
Tuning the Adsorption Properties of UiO-66 via Ligand Functionalization
Summary:
The authors from Georgia Institute of Technology and University of California, San Diego developed a series of functionalized UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with tunable adsorption properties, achieving enhanced CO₂ capture and gas separation performance.
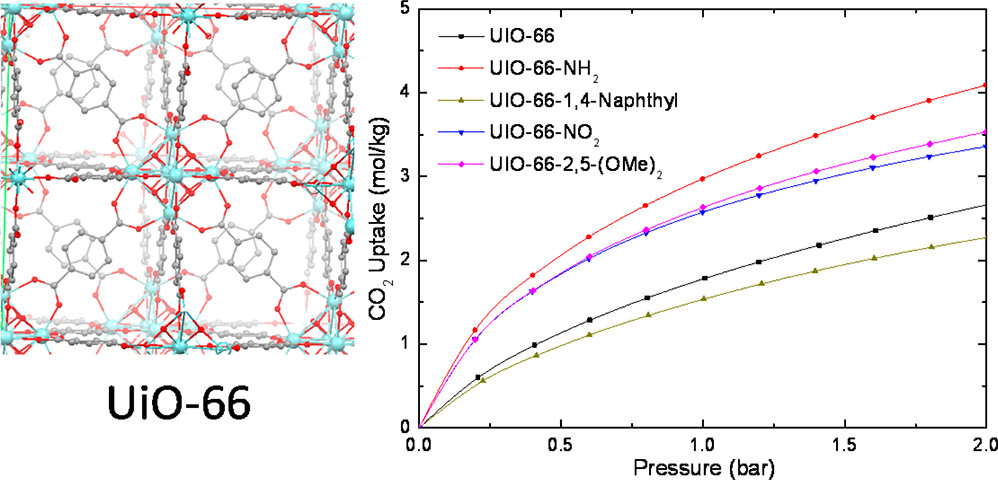
Background:
1. To address the challenge of efficient CO₂ capture and gas separation, previous researchers explored various MOFs, achieving high capacity and selectivity, yet many frameworks suffer from instability under humid conditions and limited tunability.
2. The authors proposed a ligand-functionalization strategy to systematically tune the adsorption behavior of the water-stable UiO-66 MOF, obtaining improved selectivity and hydrophobicity.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized UiO-66 and its functionalized variants (–NH₂, –NO₂, –OMe, and naphthyl) via solvothermal methods using substituted terephthalic acid ligands.
2. Characterizations:
1) BET surface areas ranged from 757 to 1123 m²/g, with reduced pore volumes in functionalized variants.
2) PXRD confirmed crystallinity and structural stability after water exposure.
3) CO₂, CH₄, N₂, and water vapor adsorption isotherms were measured; amino-functionalized UiO-66 showed the highest CO₂ uptake and selectivity.
3. Application:
The materials were tested for CO₂/CH₄ and CO₂/N₂ separation. UiO-66-NH₂ exhibited the best performance, while naphthyl-functionalized UiO-66 showed reduced water uptake and maintained reasonable selectivity.
4. Mechanism:
Enhanced CO₂ adsorption was attributed to the dipole moment and small size of polar functional groups. Water adsorption was influenced by hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of the ligands. Isosteric heats of adsorption were calculated to quantify interaction strengths.
Outlook:
This work demonstrates a versatile approach to tuning MOF adsorption properties via ligand functionalization, offering promising candidates for gas separation under both dry and humid conditions.
Tuning the Adsorption Properties of UiO-66 via Ligand Functionalization
Authors: Gregory E. Cmarik, Min Kim, Seth M. Cohen, Krista S. Walton
DOI: 10.1021/la3035352
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/la3035352
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.
