Home >
News > Multifunctional magnesium-organic framework doped biodegradable bone cement for antibacterial growth, inflammatory regulation and osteogenic differentiation
Multifunctional magnesium-organic framework doped biodegradable bone cement for antibacterial growth, inflammatory regulation and osteogenic differentiation
Summary:
The authors from Sichuan University developed a multifunctional magnesium-gallate MOF (Mg-MOF) doped biodegradable bone cement (CS/CC/DCPA) with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and osteogenic capabilities, achieving >90 % S. aureus killing within 4 h and 32 MPa compressive strength for non-load-bearing bone defect repair.
Background:
1. To treat large bone defects, previous degradable cements based on calcium sulfate (CS) showed good plasticity but rapid resorption, weak mechanics and lack of antibacterial/anti-inflammatory functions; antibiotic loading often compromises mechanical integrity.
2. The authors proposed incorporating Mg-MOF (bio-sourced gallic acid linker) into CS/CC/DCPA matrix, obtaining a self-setting cement that simultaneously enhances strength, suppresses bacteria, modulates macrophage polarization and promotes osteogenesis.
Research Content:
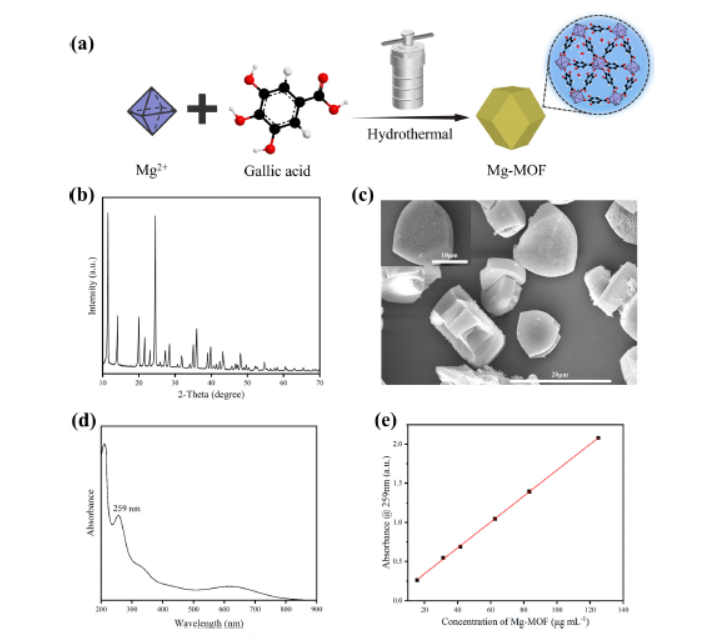
1. Synthesis:
Hydrothermal reaction of MgCl₂·6H₂O + gallic acid (pH 8–9, 120 °C, 60 h) → 10–15 µm Mg-MOF blocks; 0.3–0.5 wt % Mg-MOF blended with CS/CC/DCPA by ball-milling (250 rpm, 2 h) and 0.3 mL g⁻¹ water to form injectable paste.
2. Characterizations:
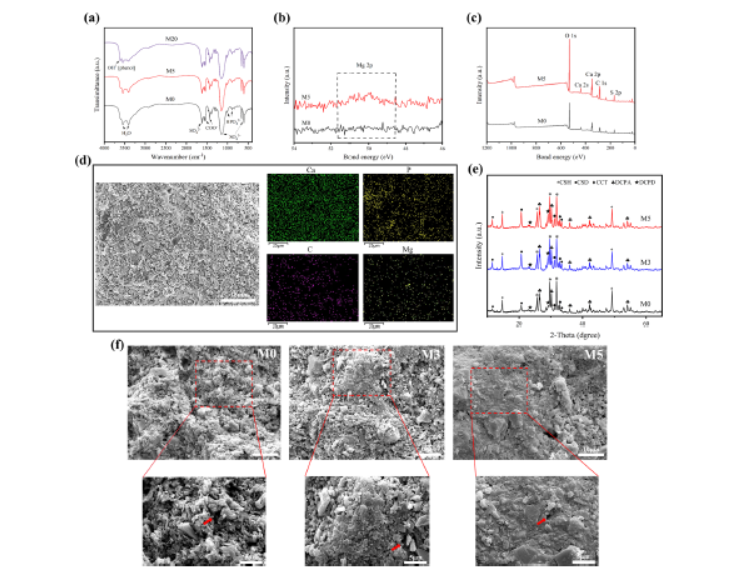
1) BET not reported; XRD confirms CS-hemihydrate, CC, DCPA/DCPD phases; MOF peaks absent due to low content.
2) SEM: Mg-MOF reduces macropores, densifies fracture surface; EDS maps uniform Mg, Ca, P distribution.
3) FT-IR & XPS verify phenolic –OH (3610 cm⁻¹) and Mg 2p signal in doped cements; UV-Vis tracks MOF release at 259 nm.
3. Application:
Setting time 27–35 min; compressive strength rises from 27 MPa (M0) to 32 MPa (M5). In PBS (37 °C, 28 d) controlled surface erosion releases 70 % Mg-MOF/Mg²⁺ within 120 h following non-Fickian diffusion. Against S. aureus & E. coli, inhibition zones 17–21 mm; S. aureus survival ≤10 % at 4 h. mBMSCs proliferation +30 % (M3), ALP & mineralized nodules up-regulated; Runx2, BMP-2, OCN, OPN, COL1 mRNA 2–4× higher than control at 14 d. LPS-stimulated macrophages: IL-6 ↓60 %, IL-10 ↑3-fold, M1→M2 polarization shift (CD86↓, CD206↑).
4. Mechanism:
Phenolic –OH from gallate disrupts bacterial membranes; released Mg²⁺ and gallic acid synergistically activate Wnt/β-catenin & BMP/Smad pathways, enhance osteoblast differentiation and ROS-scavenge to damp inflammation; smaller cement pores increase mechanical integrity.
Outlook:
Mg-MOF doped cement offers a single-phase, antibiotic-free scaffold that integrates strength, infection-prevention, immune-modulation and osteoinduction, providing a clinically translatable solution for infected or inflammatory bone defects.
Multifunctional magnesium-organic framework doped biodegradable bone cement for antibacterial growth, inflammatory regulation and osteogenic differentiation
Authors: B. Wang, H. Chen, S. Peng, X. Li, X. Liu, H. Ren, Y. Yan, Q. Zhang
DOI: 10.1039/d2tb02705d
Link: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2023/tb/d2tb02705d
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

