Home >
News > Interrogating the Metal Identity Effect of Isostructural NU-1801 Frameworks on Toxic Gas Capture with Moisture-Enhanced Feature
Interrogating the Metal Identity Effect of Isostructural NU-1801 Frameworks on Toxic Gas Capture with Moisture-Enhanced Feature
Summary:
The authors from Northwestern University, South China University of Technology, University of Jinan, Qingdao University of Science & Technology, and the U.S. Army Chemical-Biological Center developed a series of isostructural NU-1801 MOFs (Y₆, Zr₆, Hf₆, Ce₆, Th₆ clusters) with moisture-enhanced toxic-gas capture, achieving record SO₂/NH₃ uptake under 80 % RH and full cycling stability.
Background:
1. To address low-concentration SO₂/NH₃ removal under humidity, previous MOFs showed limited hydrolytic stability or competitive water adsorption.
2. The authors proposed a reticular-chemistry platform that isolates metal-identity effects and identified NU-1801(Zr) as the optimal sorbent.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis: solvothermal self-assembly of H₄TCBB with MCl₄ or M(NO₃)ₓ salts using 2-FBA/AA/FA modulators.
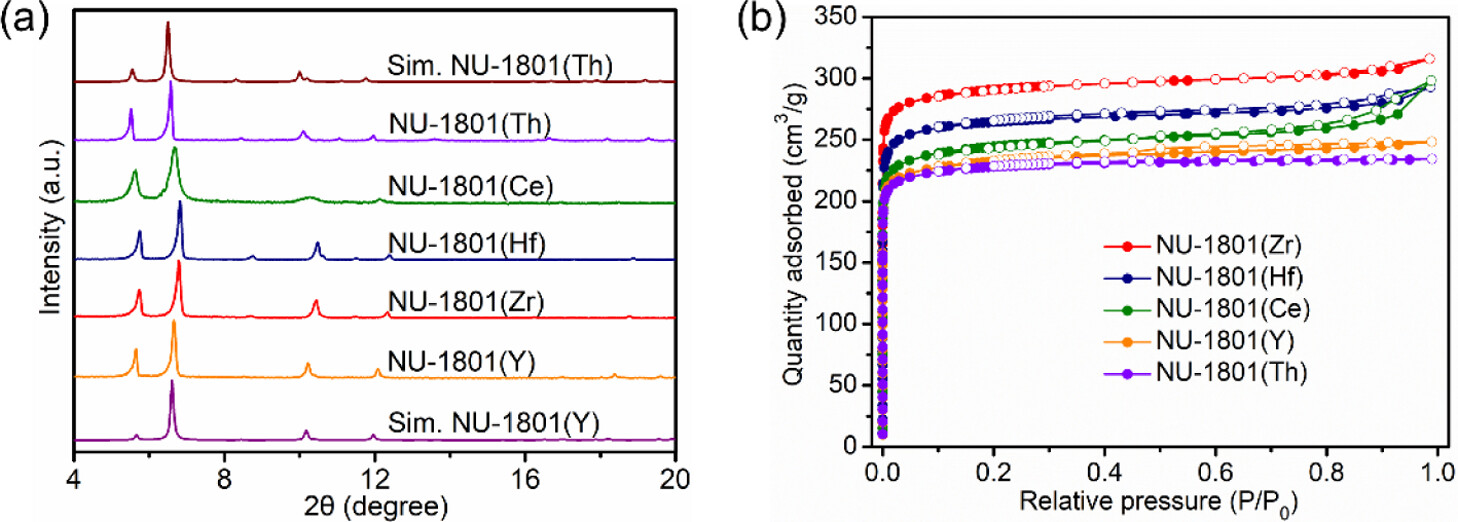
2. Characterizations:
1) BET 920–1180 m² g⁻¹, 6–10 Å pores;
2) SEM octahedral crystals (≈1 µm) except Ce;
3) XPS confirms Zr(IV), Hf(IV), Th(IV), mixed Ce(III/IV); TGA > 400 °C stability.
3. Application: 298 K breakthrough—NU-1801(Zr) captures 0.5 mmol g⁻¹ SO₂ (2.5× dry) and 1.9 mmol g⁻¹ NH₃ at 80 % RH, 1000–2000 mg m⁻³ feed.
4. Mechanism: in-situ IR shows SO₂ → SO₄²⁻ (1386, 1091, 907 cm⁻¹) and NH₃ → NH₄⁺ (3333, 1543 cm⁻¹) inside pores; DFT reveals μ₃-OH as primary binding site, coadsorption of H₂O+SO₂/NH₃ more favorable (−1.04/−19.48 kJ mol⁻¹) than water network alone.
Outlook:
The work delivers design rules for metal-cluster selection in robust MOF sorbents and opens a moisture-assisted pathway for trace toxic-gas remediation.
Interrogating the Metal Identity Effect of Isostructural NU-1801 Frameworks on Toxic Gas Capture with Moisture-Enhanced Feature
Authors: Chenghui Zhang, Yi Xie, Haomiao Xie, Xiaoliang Wang, Fanrui Sha, Kent O. Kirlikovali, Xingjie Wang, Yongwei Chen, Gregory W. Peterson, Omar K. Farha
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5c17377
Link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5c17377
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

