Home >
News > MOF-Based Refinement of Fatty Acid Derivatives
MOF-Based Refinement of Fatty Acid Derivatives
Summary:
The authors from the University of Tokyo & ADEKA Corp.: developed two isoreticular pillared-layer MOFs (1 and 2) with sub-nm channels (7.5 Å and 5.7 Å), achieving >99 % removal of carcinogenic 3-MCPDE/GE from edible oils and baseline resolution of C18-FAME E/Z and positional isomers by LC.
Background:
1. To address the problem that GC is destructive and RP-LC cannot resolve E/Z or C=C positional isomers of fatty-acid derivatives, previous researchers tried advanced ODS or cholester columns, yet Rs ≤ 0.11 was too low and prep-scale purification of oil contaminants remains inefficient.
2. The authors herein proposed a nanopore-insertion recognition strategy using configurable MOF channels and obtained record Rs = 1.25–1.79 for trans-9/trans-11 and trans-6/trans-9, plus >99 % adsorptive decontamination of palm oil.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors solvothermally synthesized [Zn2(bdc)2(ted)]n (1) and [Zn2(ndc)2(ted)]n (2) (bdc = 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate, ndc = 1,4-naphthalenedicarboxylate, ted = triethylenediamine) in DMF at 120 °C, 48 h, gram-scale.
2. Characterizations:
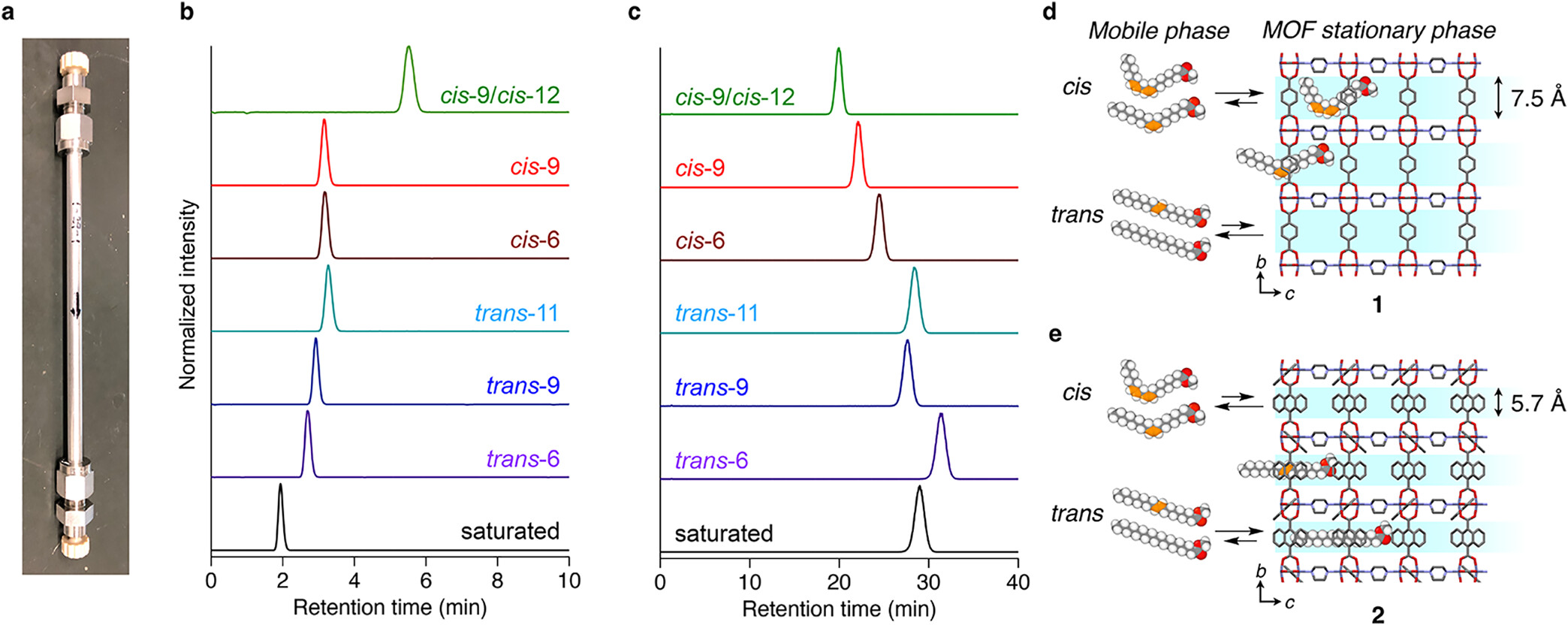
1) N2 sorption gives BET 1 850 m2 g-1 (1) and 720 m2 g-1 (2); pore size 7.5 × 7.5 Å (1) and 5.7 × 5.7 Å (2) along c-axis.
2) SEM shows ground particles 6.8 ± 2.3 µm (1) and 6.8 ± 3.7 µm (2); PXRD confirms pillared-layer tetragonal lattice retention after packing and recycling.
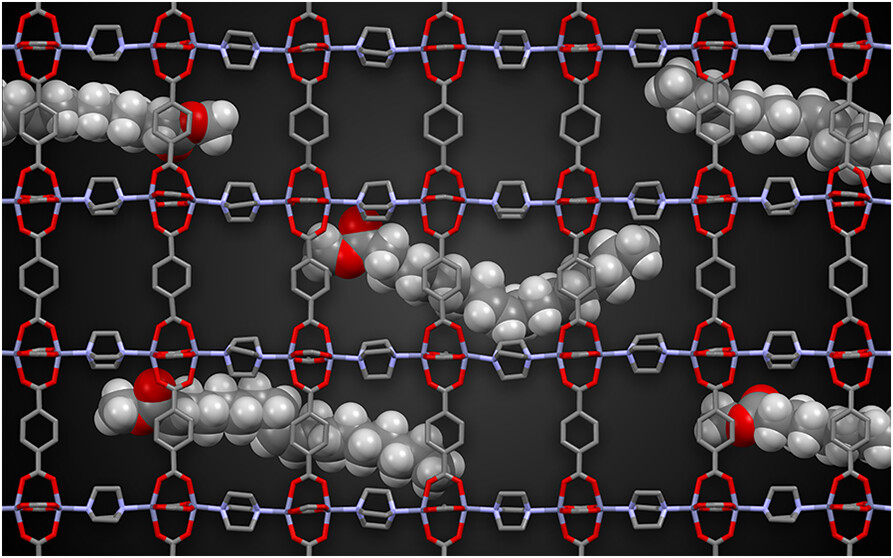
3) van’t Hoff plots (40–80 °C) reveal enthalpy-driven adsorption (ΔH −12 to −22 kJ mol-1); MD simulations (100 ns, 313 K) map dual-site C=O⋯ted (Site A) and C=C⋯ndc (Site B) interactions unique to trans-6.
3. Application:
MOF-packed 4.0 × 150 mm LC columns separate seven C18-FAMEs in 10 min (hexane, 1 mL min-1, 40 °C); Rs trans-9/trans-11 = 1.25 surpasses commercial columns by 11×. Batch adsorption with 20 wt % 2 at 90 °C, 100 Torr reduces 3-MCPDE (3.35 ppm) and GE (0.045 ppm) to below EU limits in 3 h; four cycles maintain >99 % efficiency.
4. Mechanism:
Sub-nm channels force FAMEs into extended/J conformations; only trans-6 bridges 7.3 Å-separated Sites A & B, maximizing multi-site C=O⋯H–N+ and π–π(C=C–ndc) interactions, whereas branched triacylglycerols are size-excluded, enabling contaminant-only insertion.
Outlook:
The work establishes programmable MOF nanopores as universal stationary phases for high-resolution, non-destructive FA isomer analysis and scalable edible-oil refining, readily integrable into industrial workflows and extendable to biomolecule separations.
High-Precision Separation and Refinement of Fatty Acid Derivatives by Metal–Organic Frameworks
Authors: Akihiro Torimoto, Daiki Ishibashi, Atsushi Yamashita, Takashi Uemura, Nobuhiko Hosono
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03316
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c03316
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

