Home >
News > MOF-Derived Porous Co/C Nanocomposites with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties
MOF-Derived Porous Co/C Nanocomposites with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties
Summary:
The authors from State Key Laboratory for Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces & Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, China developed porous Co/C nanocomposites with highly porous structure and ferromagnetic properties, achieving excellent electromagnetic wave absorption results (max RL -35.3 dB, effective bandwidth 5.80 GHz) in the application of electromagnetic wave absorption field.
Background:
1. To address the problems of electromagnetic radiation interference and harm, as well as the defects of single electromagnetic wave absorption materials (e.g., narrow frequency range of ferromagnetic metals, insufficient absorption intensity of carbon materials), previous researchers explored multielement composites, yet faced challenges in precisely controlling the constituent and architecture of porous materials.
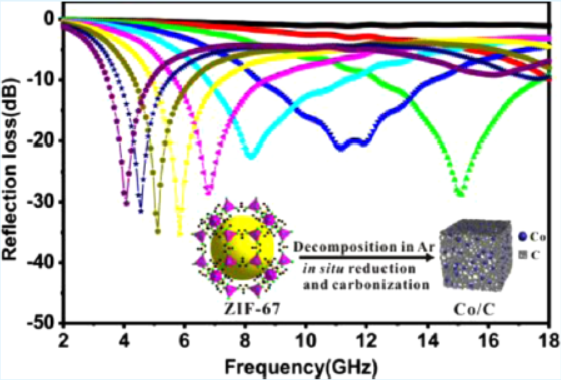
2. The authors in this study proposed an innovative method of thermal decomposition of Co-based MOF (ZIF-67) under inert atmosphere, successfully fabricating porous Co/C composites with optimized electromagnetic wave absorption performance.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized porous Co/C composites via thermal decomposition of ZIF-67 (prepared by precipitating Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O and 2-methylimidazole in methanol) under Ar atmosphere, heating at 5°C·min⁻¹ to 500-800°C and holding for 5 h.
2. Characterizations:
1) BET results: Specific surface areas are 204.7 m²/g (Co/C-500), 249.8 m²/g (Co/C-600), 234.3 m²/g (Co/C-800); type-IV isotherm with H4 hysteresis loop indicates mesoporous structure.
2) SEM/TEM tests show the particle size: Co/C-500 and Co/C-600 maintain rhombic dodecahedral shape (size shrinks), Co/C-800 agglomerates; primary crystallite sizes are ~6 nm (Co/C-500), ~10 nm (Co/C-600), ~20 nm (Co/C-800).
3) Other tests: XRD confirms fcc Co (peaks at 44.2°, 51.5°, 75.9°); VSM shows Ms:14.5-80.4 emu/g, Hc:66.1-221.6 Oe; electromagnetic tests: Co/C-500 has ε' 7.04-11.35, good impedance matching.
3. Application:
The material was tested in electromagnetic wave absorption; Co/C-500 has max RL -35.3 dB (5.8 GHz, 4 mm) and effective bandwidth 5.80 GHz (8.40-14.20 GHz, 2.5 mm); Co/C-600 and Co/C-800 perform worse.
4. Mechanism:
Porous structure reduces effective permittivity for good impedance matching; Co provides magnetic loss, carbon offers dielectric loss; multi-interfaces enhance interfacial polarization; insulating CoO reduces eddy current loss, synergistically improving absorption.

Outlook:
This research successfully develops a facile MOF-derived strategy for porous Co/C composites, realizing excellent electromagnetic wave absorption, which provides a new path for lightweight, high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber preparation and promotes related material research.
MOF-Derived Porous Co/C Nanocomposites with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties
Authors: Yinyun Lu, Yiting Wang, Hongli Li, Yuan Lin, Zhiyuan Jiang, Zhaoxiong Xie, Qin Kuang*, Lansun Zheng
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b03177
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.5b03177
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

