Home >
News > 3D Nanoporous C/Co₃O₄ Electrodes for Asymmetric Supercapacitors
3D Nanoporous C/Co₃O₄ Electrodes for Asymmetric Supercapacitors
Summary:
The authors from National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), Waseda University, etc. developed **nanoporous carbon and nanoporous Co₃O₄** with high specific surface area, good conductivity, and 3D porous structure, achieving excellent performance in asymmetric supercapacitor energy storage applications.
Background:
1. To address the problem of low energy density of supercapacitors and complex synthesis of Co₃O₄ nanostructures, previous researchers developed metal oxide-based pseudocapacitive materials and asymmetric configurations, yet faced issues like poor reproducibility and uncoordinated positive/negative electrode performance.
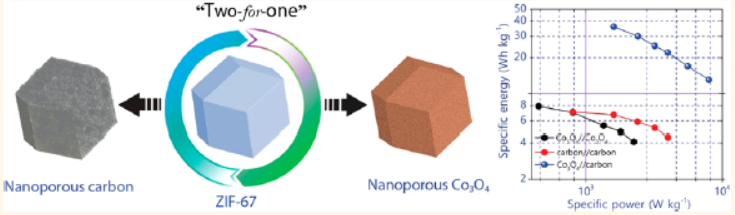
2. The authors proposed a "two-for-one" innovative method, using ZIF-67 as a single precursor to selectively prepare both electrode materials via optimized annealing, realizing synergistic improvement of supercapacitor performance.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis
- ZIF-67 precursor: CoCl₂ and 2-methylimidazole were dissolved in methanol with PVP, mixed, stirred for 1 h, aged at room temperature for 24 h, washed and dried.
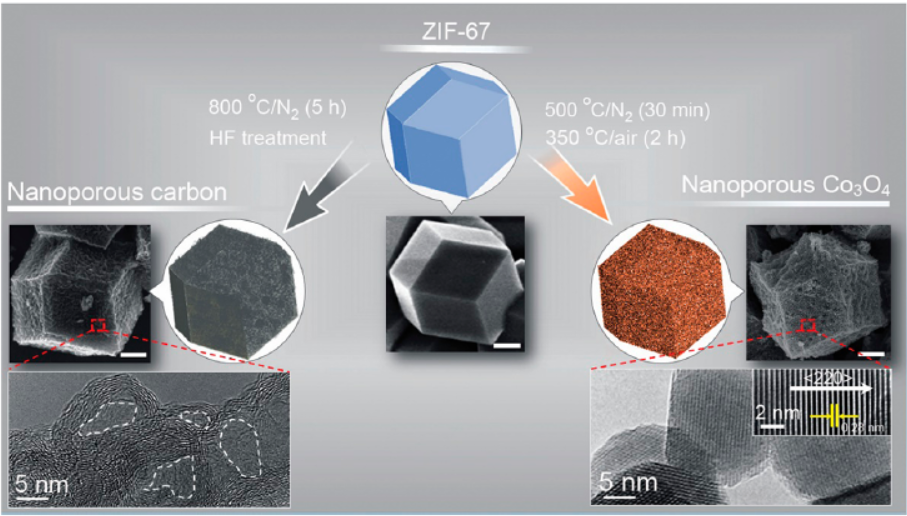
- Nanoporous carbon: ZIF-67 was carbonized at 800℃ in N₂ for 5 h, followed by HF treatment to remove Co nanoparticles.
- Nanoporous Co₃O₄: ZIF-67 was preheated at 500℃ in N₂ for 30 min, then calcined at 350℃ in air for 2 h.
2. Characterizations
1) BET and pore size: Nanoporous carbon had a specific surface area of 350 m²·g⁻¹, with pore sizes centered at 3 nm and 5-15 nm; Co₃O₄ had a specific surface area of 148 m²·g⁻¹, mainly mesoporous.
2) SEM/TEM: Both retained ZIF-67 polyhedral morphology; Co₃O₄ surface had 15-20 nm nanocrystals, carbon had nanopores after HF treatment.
3) Other tests: XRD confirmed graphitic carbon (002, 101 planes) and cubic Co₃O₄ (JCPDS 42-1467); XPS showed carbon contained 90.8 at% C and 5.1 at% N, Co₃O₄ contained 36.9 at% Co and 57.4 at% O.
3. Application
- As supercapacitor electrodes: Carbon had a capacitance of 272 F·g⁻¹, Co₃O₄ had 504 F·g⁻¹ at 5 mV·s⁻¹.
- Asymmetric supercapacitor (Co₃O₄//carbon): Operated at 0.0-1.6 V, specific energy of 36 W·h·kg⁻¹, maximum specific power of 8000 W·kg⁻¹, 89% capacitance retention after 2000 cycles.
4. Mechanism
- High specific surface area provides abundant reaction sites; 3D porous structure accelerates ion diffusion and charge transfer.
- Carbon acts as EDLC electrode (wide potential window), Co₃O₄ as pseudocapacitive electrode (redox reaction with OH⁻), synergistically enhancing energy and power density.
Outlook:
This research realizes the preparation of two high-performance electrode materials from a single precursor, simplifying the synthesis process and improving supercapacitor performance, which is of great significance for the development of low-cost, high-efficiency energy storage devices.
Asymmetric Supercapacitors Using 3D Nanoporous Carbon and Cobalt Oxide Electrodes Synthesized from a Single Metal-Organic Framework
Authors: Rahul R. Salunkhe, Jing Tang, Yuichiro Kamachi, Teruyuki Nakato, Jung Ho Kim, Yusuke Yamauchi
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01790
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.5b01790
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

