Home >
News > NIR-Inhibited Aβ Aggregation Neurotoxicity
NIR-Inhibited Aβ Aggregation Neurotoxicity
Summary:
The authors from Department of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (Hong Kong S.A.R. China) and Department of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology University (Australia) developed PCN-224 nanoparticles (porphyrinic metal-organic framework) with high photo-oxygenation efficiency, good biocompatibility and stability, achieving effective inhibition of Aβ₄₂ aggregation and reduction of its neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) treatment application.
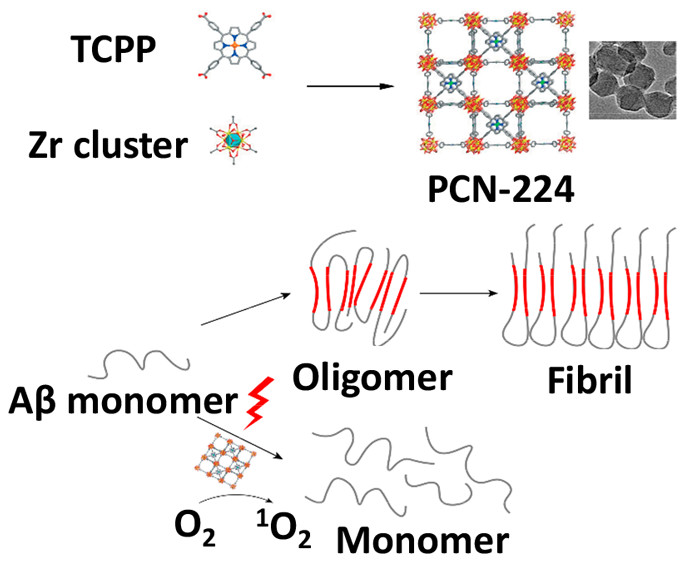
Background:
1. To address the problem of abnormal Aβ aggregation causing AD and the limitations of existing Aβ aggregation inhibitors (organic photosensitizers with poor water dispersity/photostability, visible light dependence; nanoparticle photosensitizers with low quantum yield), previous researchers used organic photosensitizers (e.g., rose bengal) and nanoparticle systems (e.g., UCNP-RB hybrid) for Aβ aggregation inhibition, achieving partial inhibition effects, yet there are problems like limited tissue penetration (visible light) and low photo-oxygenation efficiency.
2. The authors in this study proposed an innovative method of synthesizing porphyrinic Zr-MOF (PCN-224) nanoparticles by coordinating TCPP ligand with Zr, obtaining results of NIR-induced efficient Aβ₄₂ aggregation inhibition and neurotoxicity reduction.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized PCN-224 by dissolving TCPP (0.02 mmol), ZrOCl₂·8H₂O (0.12 mmol) and benzoic acid (1.76 mmol) in DMF, heating at 90℃ for 5 h (300 rpm stirring), followed by centrifugation (21,120 g, 30 min), washing (DMF/ethanol, 3 times) and freeze-drying; Aβ₄₂ was prepared via HFIP dissolution, nitrogen drying and DMSO/HEPES dilution.
2. Characterizations:
1) BET result: PCN-224 has a specific surface area of 326.34 m²/g; pore size distribution not explicitly given but confirmed porous via N₂ adsorption-desorption isotherms.
2) SEM/TEM tests show the particle size of the material is around 70 nm (round shape).
3) Optical tests: UV-vis has 425 nm main peak and 500-700 nm Q bands; fluorescence quantum yield 17%, emission peak 680 nm; zeta potential +25.8 mV (water)、-24.5 mV (HEPES, pH7.4); PXRD confirms crystalline stability.
3. Application:
The material was tested in Aβ₄₂ aggregation inhibition (650 nm light, 30 mW/cm², 30 min irradiation) and PC12 cell cytotoxicity assays; results: ThT fluorescence intensity reduced, Aβ₄₂ fibril formation inhibited; cell viability of Aβ₄₂-treated group increased to 90%.
4. Mechanism:
Experiment result analysis: PCN-224 generates ¹O₂ under NIR (confirmed by DPBF/DCFH-DA/ESR), oxidizes Aβ₄₂ (DNPH assay detects carbonyl groups), preventing β-sheet formation; mechanism reasoning: TCPP ligands in MOF avoid self-quenching, porous structure facilitates O₂ diffusion, enhancing photo-oxygenation efficiency.

Outlook:
This research successfully develops NIR-responsive PCN-224 nanoparticles, solving key limitations of traditional Aβ inhibitors, and provides a new non-invasive phototherapeutic strategy for AD, with significant value for neurodegenerative disease treatment research.
Porphyrinic Metal-organic Framework PCN224 Nanoparticles for Near-IR Induced Attenuation of Aggregation and Neurotoxicity of Alzheimer’s Amyloid-β Peptide
Authors: Jiuhai Wang, Yadi Fan, Youhua Tan, Xin Zhao, Yu Zhang, Changming Cheng, Mo Yang
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b15452
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.8b15452
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

