Home >
News > Synthesis of defective MOF-801 via an environmentally benign approach for diclofenac removal from water streams
Synthesis of defective MOF-801 via an environmentally benign approach for diclofenac removal from water streams
Summary:
The authors from Imperial College London developed defective MOF-801 (d-MOF-801) with adjustable defects, high specific surface area, and excellent adsorption capacity, achieving a maximum diclofenac adsorption capacity of 680 mg/g in water pollutant removal.
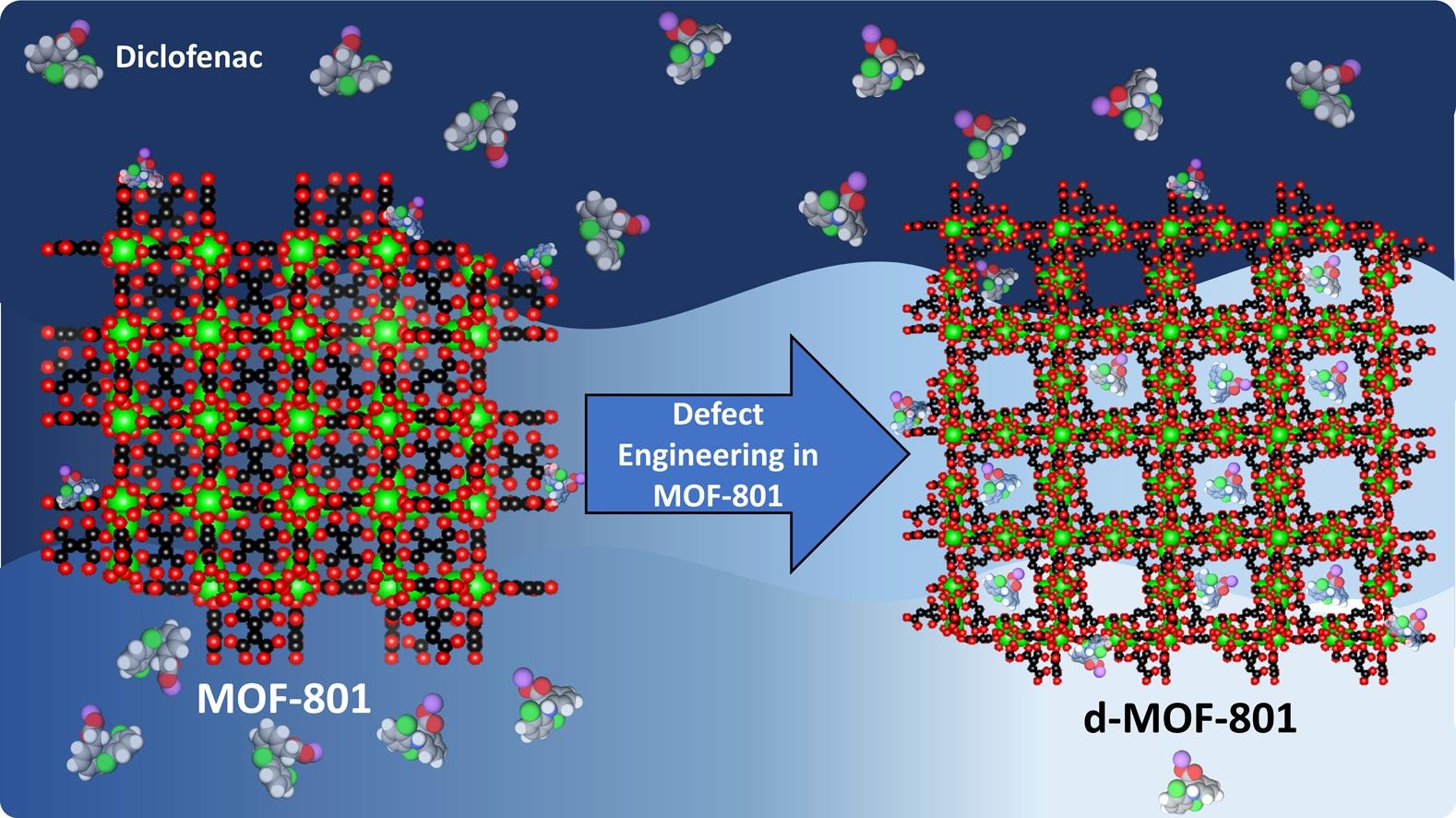
Background:
1. To address diclofenac pollution harming aquatic ecosystems, previous researchers used adsorbents like activated carbon (100-200 mg/g capacity) and MOFs (needing complex post-modification), which had low capacity or high synthesis complexity.
2. The authors proposed an eco-friendly aqueous room-temperature synthesis, adjusting formic acid dosage to tune defects in MOF-801, realizing 4x higher adsorption capacity without post-modification.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
d-MOF-801: 350 mg ZrCl₄ + 160 mg fumaric acid dissolved in 8 mL water, added 2-4 mL formic acid, sonicated 1 h, stood at room temperature 24 h, centrifuged, washed, dried. MOF-801: 120 mg ZrCl₄ + 180 mg fumaric acid in 20 mL DMF, 120℃ solvothermal reaction 24 h.
2. Characterizations:
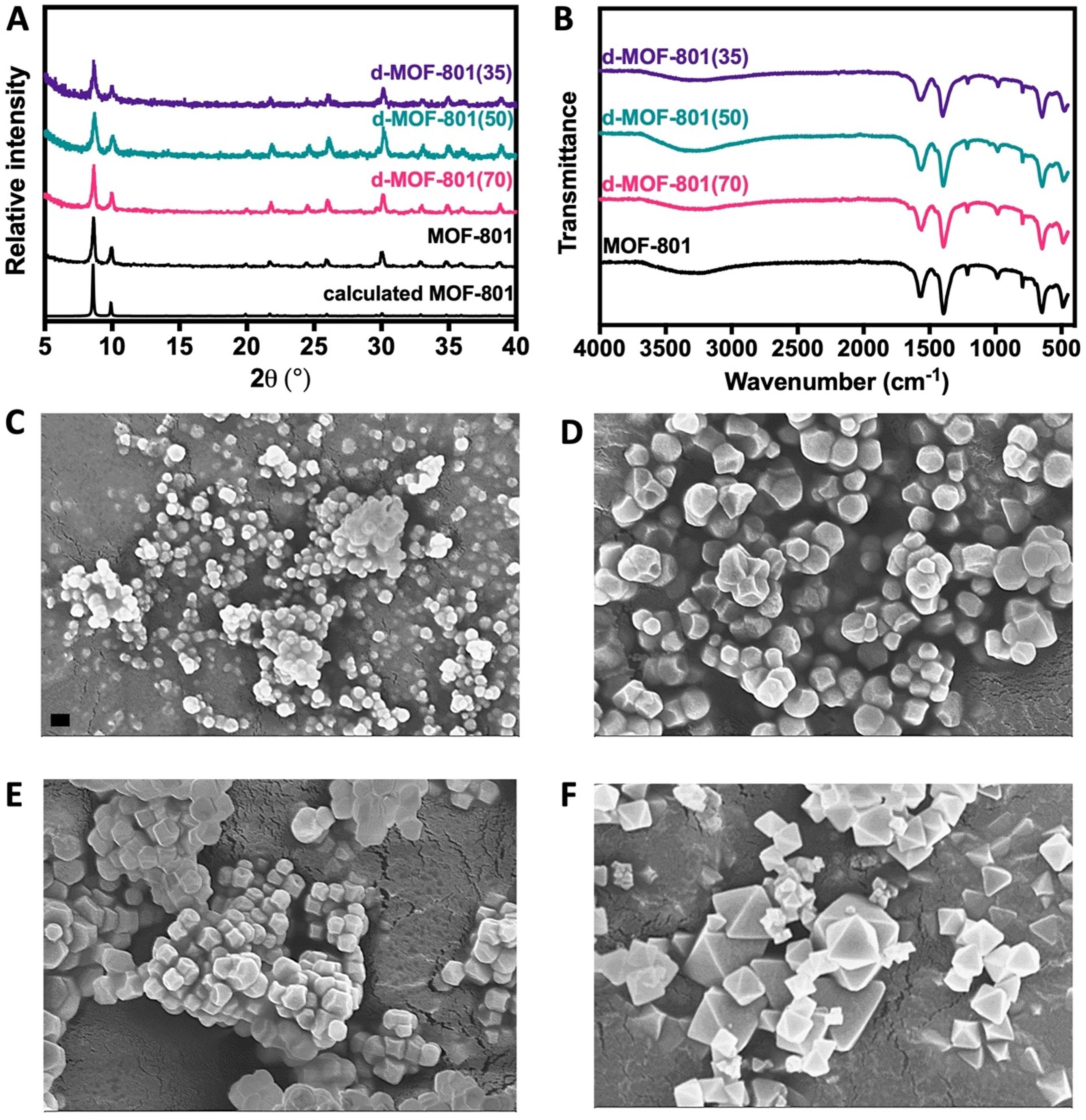
1) BET: d-MOF-801(35) had 1070 m²/g surface area, 1.126 nm pore width, 0.37 cm³/g pore volume; MOF-801 had 811 m²/g, 0.524 nm, 0.28 cm³/g.
2) SEM: d-MOF-801 was spherical (<200 nm), MOF-801 was octahedral (~500 nm).
3) PXRD confirmed MOF-801 crystallinity; FTIR showed carboxylate peaks at 1390/1550 cm⁻¹.
3. Application:
Tested in diclofenac adsorption: d-MOF-801(35) reached equilibrium in <1 h, retained ~600 mg/g capacity after 4 cycles; stable in 6-10 pH, less affected by chloride salts.
4. Mechanism:
Defects enlarged pores (1.2 nm) for diclofenac access; d-MOF-801’s positive zeta potential enhanced electrostatic/cation-π interactions with diclofenac anions.
Outlook:
This research developed an eco-friendly defective MOF synthesis, significantly improving adsorption performance. It provides a high-efficiency adsorbent for water decontamination and promotes green MOF applications in environmental remediation.
Synthesis of defective MOF-801 via an environmentally benign approach for diclofenac removal from water streams
Authors: Nicholaus Prasetya, Kang Li
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122024
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383586622015799
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

