Home >
News > Water Adsorption in Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks
Water Adsorption in Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks
Summary:
The authors from the University of California – Berkeley, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and National Institute of Standards and Technology (United States) developed Zr-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with low-pressure steep water adsorption, high capacity, and recyclability, achieving excellent performance in water capture and thermal battery applications.
Background:
1. To address the issues of high regeneration energy consumption for zeolites, high humidity requirement for mesoporous materials, and poor balance of low-pressure adsorption, high capacity, and cyclic stability for existing MOFs, previous researchers studied water adsorption of porous materials like zeolites and MOFs, yet failed to meet all three key criteria for water adsorption.
2. The authors proposed an innovative method of designing Zr-based MOFs with varied pore sizes and topologies via solvothermal synthesis, obtaining materials (e.g., MOF-801-P, MOF-841) with outstanding water adsorption performance.
Research Content:
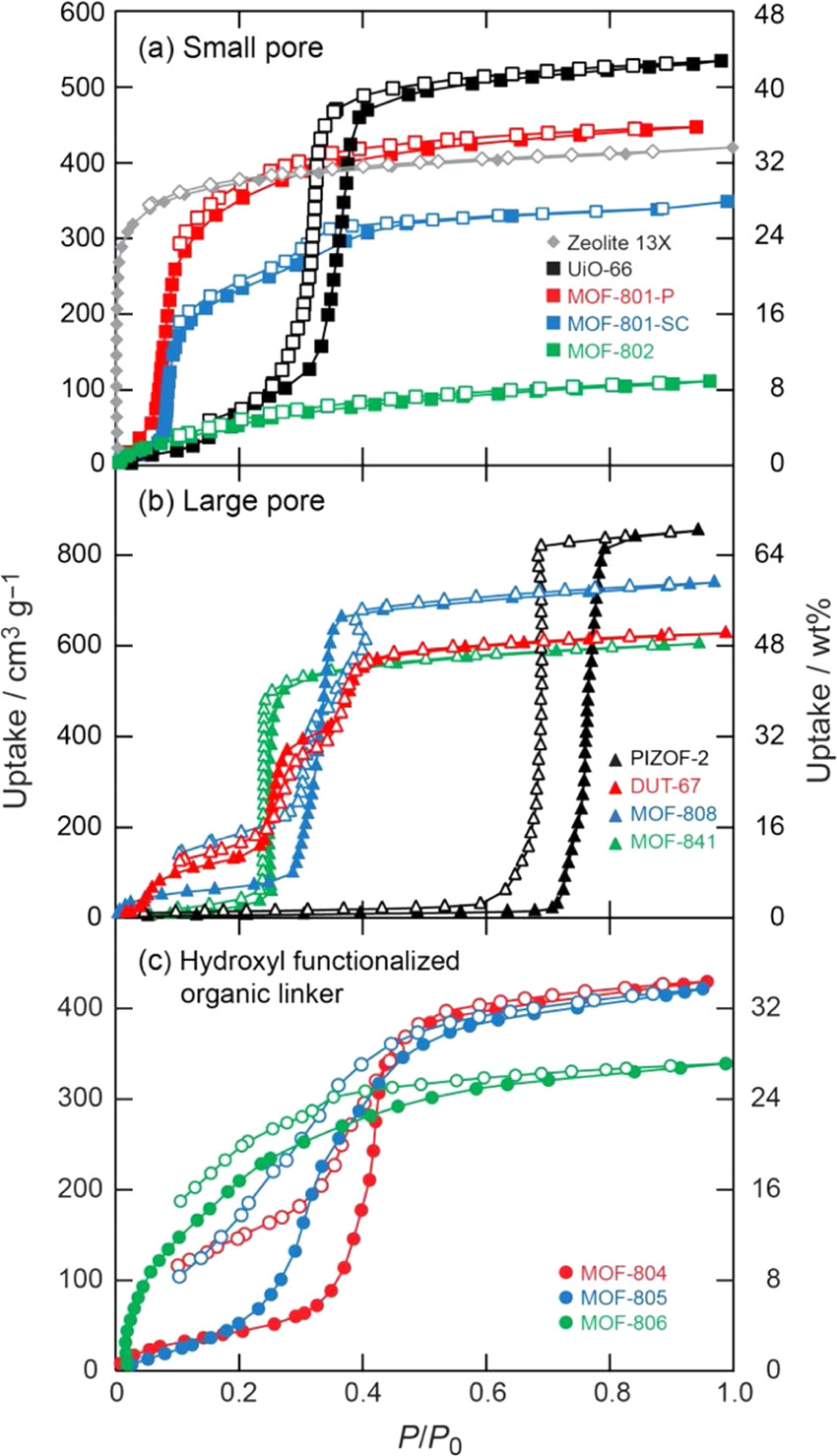
1.Synthesis: The authors synthesized 10 Zr-based MOFs (7 new ones, e.g., MOF-802, MOF-841) using solvothermal method, with ZrOCl₂·8H₂O as metal source and various carboxylic acids (fumaric acid, H₂PZDC) as linkers, followed by solvent exchange and supercritical CO₂ activation.
2.Characterizations:
1) BET: MOF-801-P (990 m²/g), MOF-841 (1390 m²/g); pore size: MOF-801-P (4.8-7.4 Å), MOF-841 (9.2 Å).
2) XRD: MOF-801-P (cubic, Pn-3), MOF-802 (orthorhombic, Fdd2).
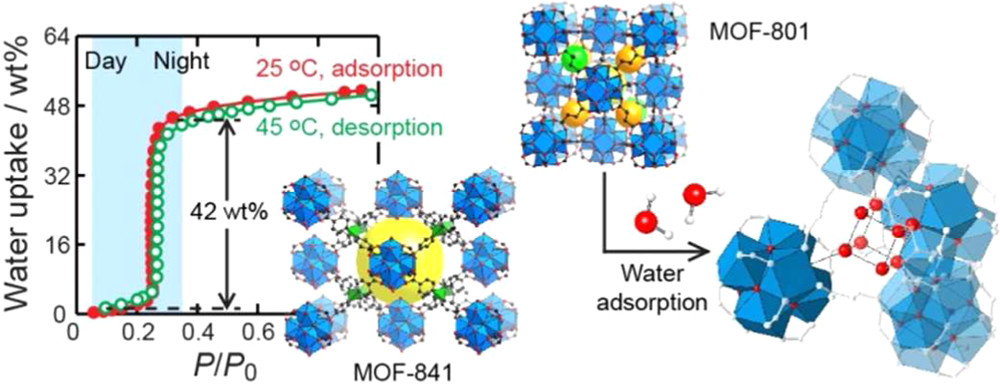
3) Water adsorption: MOF-801-P (22.5 wt% at P/P₀=0.1), MOF-841 (44 wt% at P/P₀=0.3), stable for 5 cycles.
3.Application: Tested in thermal batteries (1.8 kW power) and desert water delivery (6.3 L/day for 15 kg MOF-841), showing good potential.
4.Mechanism: Neutron/XRD revealed 5 adsorption sites; water molecules form hydrogen-bonded clusters in pores, optimizing adsorption.
Outlook:
This research develops high-performance Zr-based MOFs for water adsorption, clarifies the structure-performance relationship, and provides new materials for thermal batteries and water capture.
Water Adsorption in Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks and Related Materials
Authors: Hiroyasu Furukawa, Felipe Gándara, Yue-Biao Zhang, Juncong Jiang, Wendy L. Queen, Matthew R. Hudson, Omar M. Yaghi
DOI: 10.1021/ja500330a
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja500330a
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

