Home >
News > Cost-Effective Zinc-Based Metal−Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Methane Purification
Cost-Effective Zinc-Based Metal−Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Methane Purification
Summary:
The authors from Foshan University and South China University of Technology developed a zinc-based metal-organic framework (CALF-20) with low cost, high stability, and tailored pores, achieving efficient separation of C₂H₆/CH₄ and CH₄/N₂ in methane purification.
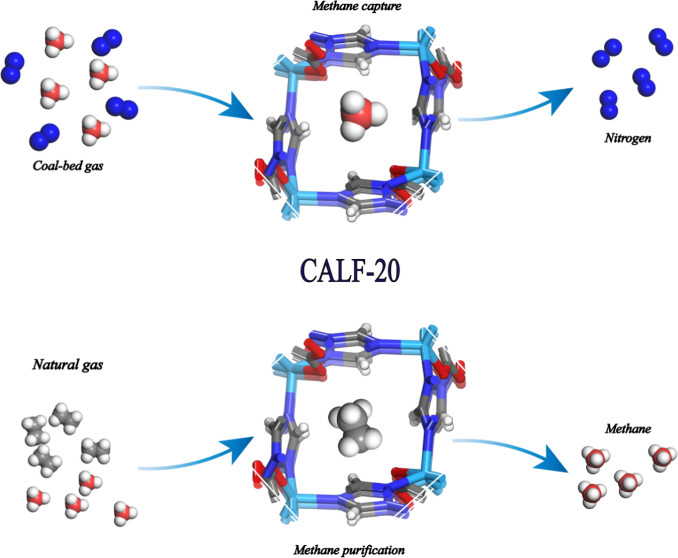
Background:
1. To address the high energy consumption of traditional distillation for methane purification and the issues of poor stability, unbalanced adsorption/selectivity, or high cost of existing MOFs, previous researchers developed MOFs like SBMOF-1 (high C₂H₆/CH₄ selectivity but low capacity) and ATC-Cu (high CH₄ uptake but poor moisture stability), yet no material balances performance, stability, and cost.
2. The authors proposed using CALF-20, optimizing its synthesis to reduce cost (ligand cost: $53/kg) and leveraging its 3D pore structure and specific interactions to achieve high separation performance with excellent stability.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis
The authors synthesized CALF-20 via a modified solvothermal method: dissolved zinc oxalate (6.60 g) in methanol (30.0 mL) and 1,2,4-triazole (5.00 g) in methanol (36.0 mL), mixed the two solutions, heated to 453 K for 48 h, filtered to get white powder, activated by soaking in methanol (40.0 mL, replaced every 12 h for 36 h), and dried under vacuum at 373 K for 12 h.
2. Characterizations
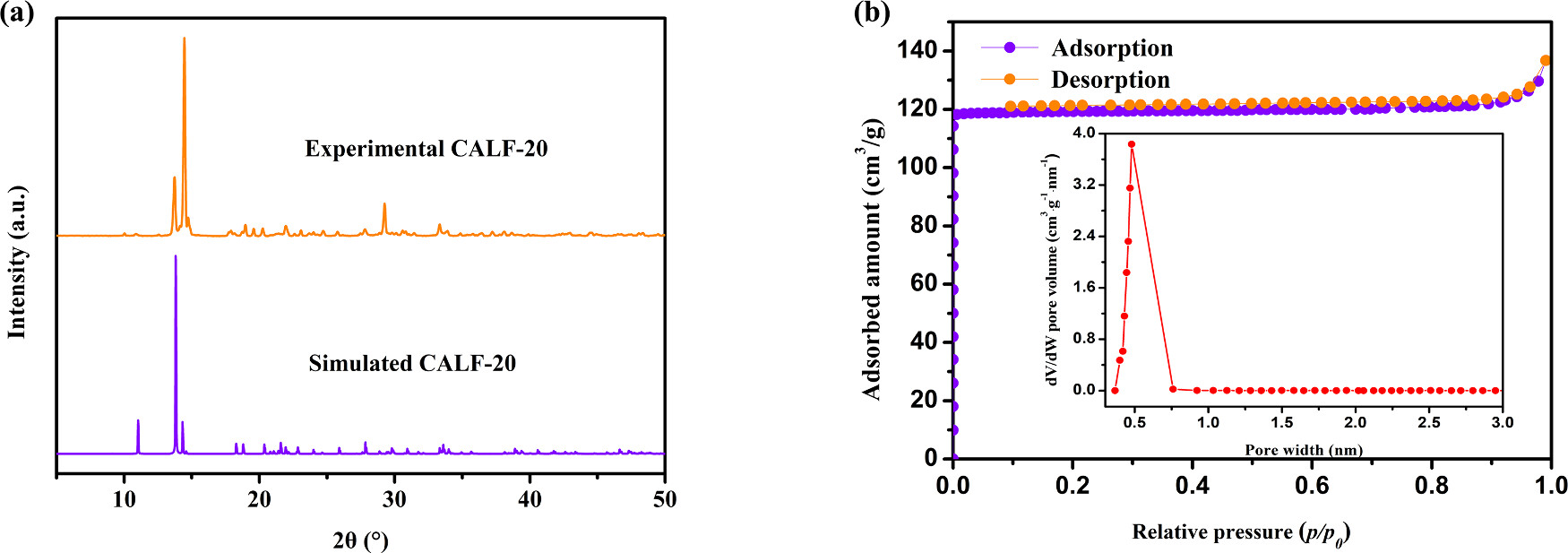
1) BET: BET specific surface area = 457.1 m²/g, Langmuir surface area = 519.4 m²/g, total pore volume = 0.21 cm³/g; pore size distribution: 0.37–0.76 nm (main peak at 0.48 nm).
2) SEM tests show CALF-20 has a regular morphology (no specific particle size value reported, but crystals have minor defects).
3) Thermal analysis: 10 wt% weight loss at ~373 K (solvent removal), stable up to 613 K; PXRD: experimental and simulated peaks match, structure intact after water/humidity treatment.
3. Application
- Static adsorption: At 298 K, 100 kPa, CH₄ uptake = 1.11 mmol/g, C₂H₆ uptake = 2.74 mmol/g, N₂ uptake = 0.41 mmol/g; C₂H₆/CH₄ selectivity = 22.7, CH₄/N₂ selectivity = 15.0 (0.5 kPa).
- Dynamic breakthrough: For equimolar mixtures, CH₄ and N₂ breakthrough time difference = 102.0 s/g; C₂H₆ retention time longer than CH₄; 5 cycles show stable performance.
4. Mechanism
- Experimental analysis: CALF-20’s micropores (0.48 nm main pore) and specific interactions (C-H···N, C-H···π) enhance affinity for C₂H₆ and CH₄ over N₂.
- Molecular simulation: Interaction energies: C₂H₆ (-29.1 kJ/mol) > CH₄ (-22 kJ/mol) > N₂ (-16.1 kJ/mol); more binding sites for CH₄/C₂H₆ explain high selectivity.
Outlook:
This research develops low-cost, stable CALF-20 with balanced adsorption/selectivity, solving key industrial methane purification issues and providing a practical adsorbent candidate for natural gas/coalbed gas processing.
Cost-Effective Zinc-Based Metal−Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Methane Purification
Authors: Jiangshang Su, Jiongfeng Li, Junhao Xu, Yongtao Li, Rou Zhang, Daofei Lv, Feng Xu, Junjie Peng, Xun Wang, Jian Yan, Zewei Liu, Xin Chen, Hongxia Xi, Qibin Xia
DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.4c02414
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.iecr.4c02414
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

