Home >
News > High-Efficiency Sandwich-Like Hierarchical AgBr-Ag@MIL-68(Fe) Photocatalysts: Step-Scheme Photocatalytic Mechanism for Enhanced Photoactivity
High-Efficiency Sandwich-Like Hierarchical AgBr-Ag@MIL-68(Fe) Photocatalysts: Step-Scheme Photocatalytic Mechanism for Enhanced Photoactivity
Summary:
The authors from Department of Chemistry, Ningde Normal University; State Key Laboratory of Photocatalysis on Energy and Environment, Fuzhou University, etc. developed sandwich-like hierarchical AgBr-Ag@MIL-68(Fe) photocatalysts with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity, achieving efficient removal of organic dyes (e.g., RhB) and heavy metal ions (Cr(VI)) in the field of environmental remediation.
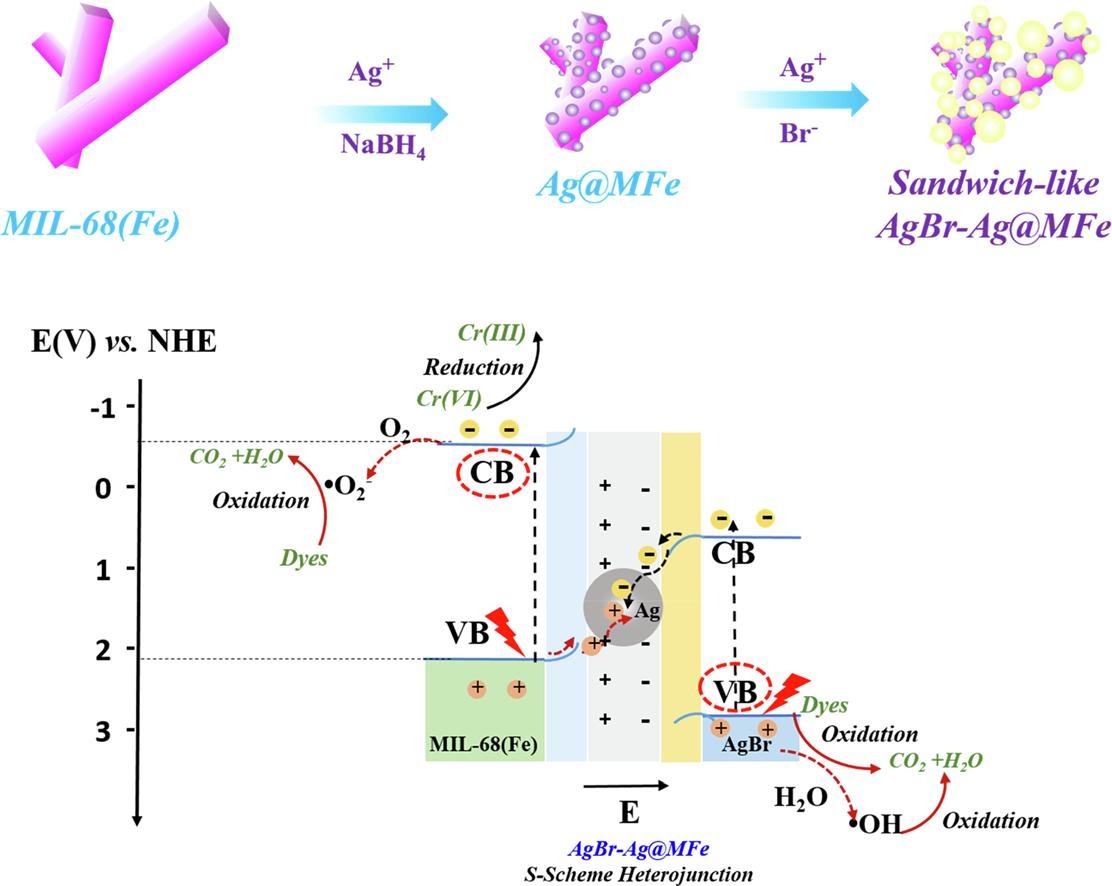
Background:
1. Organic pollutants and heavy metals in water pose serious risks, but traditional photocatalysts suffer from low visible-light response and high charge recombination rates. MOF-based heterojunctions often have weakened redox ability, limiting their performance.
2. The authors proposed a novel impregnation–precipitation method to construct S-scheme AgBr-Ag@MIL-68(Fe) photocatalysts, which efficiently separate charges while retaining strong redox capacity, achieving enhanced bifunctional photocatalytic activity.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized MIL-68(Fe) via solvothermal method using FeCl₃·6H₂O and 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (H₂BDC). Ag@MIL-68(Fe) was prepared by impregnating AgNO₃ followed by NaBH₄ reduction. AgBr-Ag@MIL-68(Fe) was obtained by precipitating AgBr on Ag@MIL-68(Fe) using KBr and AgNO₃.
2. Characterizations:
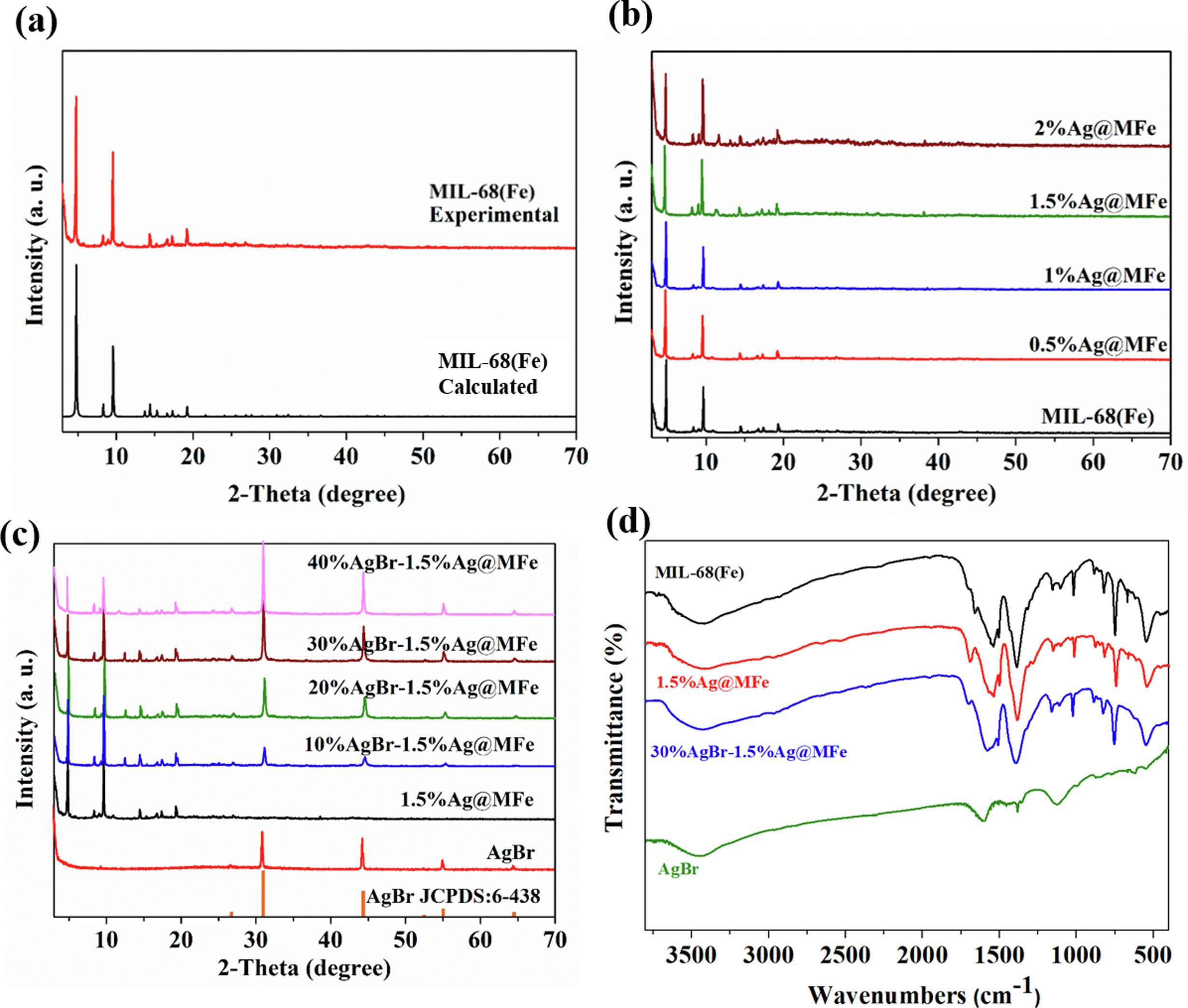
1) BET results showed MIL-68(Fe) had a surface area of 527 m²/g, which decreased with Ag and AgBr loading (30%AgBr-1.5%Ag@MFe: 249 m²/g).
2) SEM/TEM tests showed MIL-68(Fe) was cuboid-like (2–3 μm); Ag NPs (5–10 nm) were uniformly distributed, and AgBr (200–450 nm) formed a sandwich structure with Ag@MIL-68(Fe).
3) UV-vis DRS showed enhanced visible-light absorption; XPS confirmed electron transfer at the interface; ESR detected •OH and •O₂⁻ radicals; transient photocurrent and EIS indicated efficient charge separation.
3. Application:
The material efficiently degraded RhB (96% in 60 min) and reduced Cr(VI) (high efficiency) under visible light. It showed good stability over four cycles and performed well in mixed systems (RhB/Cr(VI)), with removal rates of 99.7% and 99.0% respectively.
4. Mechanism:
An S-scheme charge transfer mechanism was proposed. Ag NPs act as electron mediators, promoting recombination of low-energy electrons (AgBr CB) and holes (MIL-68(Fe) VB), while retaining high-energy electrons (MIL-68(Fe) CB) for Cr(VI) reduction and holes (AgBr VB) for dye oxidation, generating •OH and •O₂⁻ radicals.
Outlook:
This research provides a feasible method to construct high-performance S-scheme photocatalysts, highlighting their potential in environmental remediation and solar energy conversion.
High-Efficiency Sandwich-Like Hierarchical AgBr-Ag@MIL-68(Fe) Photocatalysts: Step-Scheme Photocatalytic Mechanism for Enhanced Photoactivity
Authors: Ruowen Liang, Zhoujun He, Yi Lu, Guiyang Yan, Ling Wu
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119442
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383586621011503
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

