Home >
News > Facile fabrication of magnetic metal–organic framework nanocomposites for potential targeted drug delivery
Facile fabrication of magnetic metal–organic framework nanocomposites for potential targeted drug delivery
Summary:
The authors from Anhui University, University of Science and Technology of China, and Chinese Academy of Sciences developed magnetic Fe₃O₄/Cu₃(BTC)₂ (HKUST-1) nanocomposites with high porosity and superparamagnetism, achieving 0.20 g g⁻¹ nimesulide loading and 11-day sustained release for targeted pancreatic-cancer therapy.
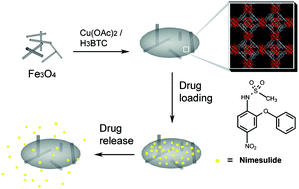
Background:
1. To address inefficient drug accumulation at tumors, previous groups exploited mesoporous silica or MIL-series MOFs, achieving high payloads yet facing complex surfactant removal, burst release, or poor magnetic guidance.
2. The authors herein propose a one-pot co-precipitation/MOF-growth strategy to embed Fe₃O₄ nanorods in Cu₃(BTC)₂ crystals, affording a surfactant-free, magnetically steerable nanocomposite with prolonged release kinetics.
Research Content:
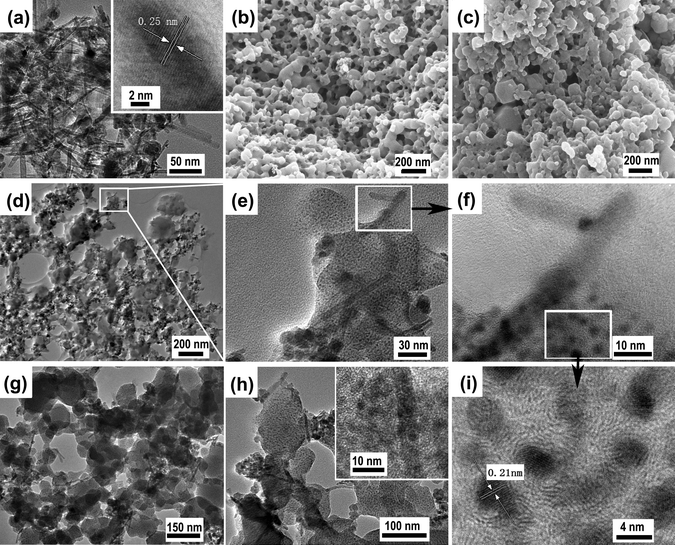
1. Synthesis: Fe₃O₄ nanorods (15 nm × 75 nm) were first generated via co-precipitation; Cu(OAc)₂ and H₃BTC were then reacted at 70 °C in DMF/EtOH/H₂O in the presence of the nanorods to produce Fe₃O₄/Cu₃(BTC)₂ nanocomposites (50–150 nm).
2. Characterizations:
1) BET surface area 517–519 m² g⁻¹, pore volume 0.29–0.32 cm³ g⁻¹; microporous channels ~9.5 Å.
2) SEM/TEM show nanorods fully encapsulated in HKUST-1 nanocrystals (3–5 nm), forming irregular composite nanoparticles.
3) VSM indicates saturation magnetization 0.92–1.54 emu g⁻¹, enabling magnetic separation within 20 s.
3. Application: The composite adsorbed 0.17–0.20 g g⁻¹ nimesulide (COX-2 inhibitor) and released >90 % over 11 days in physiological saline at 37 °C under a Higuchi diffusion model.
4. Mechanism: Drug molecules diffuse along the diagonal (13.3 Å) of HKUST-1 square channels; π–π stacking and Cu–amino coordination slow the final 10 % release, avoiding burst profiles observed in surface-adsorbed systems.
Outlook:
This work provides a facile, green route to magnetic MOF nanocomposites, validating the concept of targeted, sustained drug delivery; extension to non-toxic Fe-carboxylate MOFs (e.g., MIL-53-Fe) is anticipated for clinical translation.
Facile fabrication of magnetic metal–organic framework nanocomposites for potential targeted drug delivery
Authors: Fei Ke, Yu-Peng Yuan, Ling-Guang Qiu, Yu-Hua Shen, An-Jian Xie, Jun-Fa Zhu, Xing-You Tian, Li-De Zhang
DOI: 10.1039/c0jm01770a
Link: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm01770a
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

