A Facile and General Coating Approach to Moisture/Water-Resistant Metal−Organic Frameworks with Intact Porosity
Summary:
The authors from the University of Science and Technology of China (Hefei, China) developed PDMS-coated moisture/water-resistant metal-organic frameworks (MOFs, including MOF-5, HKUST-1, ZnBT) with intact porosity, achieving excellent performance in CO₂ sorption and heterogeneous catalysis.
 Background:
Background:
1. To address the poor moisture/water stability of most MOFs (a key barrier to practical application), previous researchers either directly synthesized stable/hydrophobic MOFs or functionalized MOFs with hydrophobic surfaces. However, these methods suffered from reduced porosity, tedious procedures, or complex instrumentation.
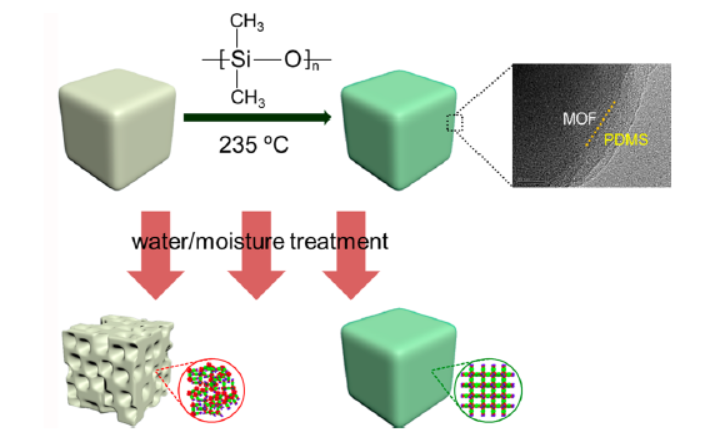
2. The authors proposed an innovative PDMS vapor deposition coating method: heating MOFs with PDMS stamps at 235°C to form a hydrophobic PDMS layer on MOF surfaces, enhancing moisture/water resistance while retaining intact porosity.
Research Content:
1.Synthesis:
-Pristine MOFs:
MOF-5 was synthesized via room-temperature reaction of terephthalic acid, triethylamine, and zinc acetate dihydrate in DMF;
HKUST-1 via solvothermal reaction of 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid and copper nitrate trihydrate (100°C, 10 h); ZnBT via solvothermal reaction of zinc nitrate hexahydrate, terephthalic acid, and triethylenediamine (120°C, 48 h). All were centrifuged and washed with DMF/CHCl₃ (or methanol).
-PDMS Coating: MOF powder was spread thinly on a glass dish, placed in a sealed container with PDMS stamps, heated at 235°C for 6 h, then cooled naturally.
2.Characterizations:
1)BET & Pore Size: MOF-5 (Sᵦₑₜ=3118 m²/g) and coated MOF-5 (3159 m²/g) retained ~100% surface area; HKUST-1 (1547 m²/g) and coated HKUST-1 (1544 m²/g) showed similar Sᵦₑₜ; ZnBT (1950 m²/g) and coated ZnBT (1845 m²/g) had minimal Sᵦₑₜ loss (Table S1).
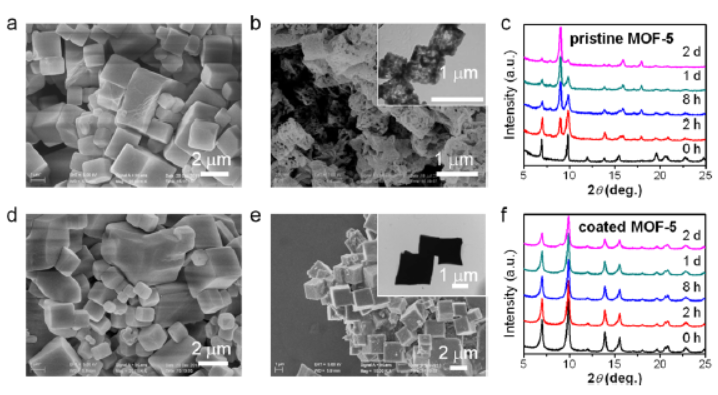
2)SEM/TEM: SEM showed pristine MOF-5/HKUST-1/ZnBT lost regular morphology after moisture/water treatment, while coated ones remained intact; HRTEM revealed an ~10 nm PDMS layer on coated MOF-5.
3)Other Tests: XRD confirmed coated MOFs retained crystallinity after treatment; XPS detected Si (from PDMS) on coated MOFs, with Cu 2p binding shift in HKUST-1 indicating Cu-O bonding with PDMS; water contact angle of coated MOFs was 130±2° (hydrophobic, vs. ~0° for pristine).
3.Application:
-CO₂ Sorption: At 273 K/760 mmHg, coated MOF-5 retained CO₂ uptake (39.5→38.8 cm³/g) after moisture treatment, while pristine MOF-5 dropped from 38.2 to 8.1 cm³/g; coated HKUST-1 (175.3→180.1 cm³/g) vs. pristine (182.2→27.4 cm³/g) (Table S2).
-Catalysis: Coated HKUST-1 had 50.1% yield in benzaldehyde-TMSCN cyanosilylation (333 K, 48 h), retaining 49.1% yield after water vapor treatment; pristine HKUST-1 dropped from 48.2% to 19.6%.
4.Mechanism:
Volatile low-molecular-weight silicone from PDMS thermal degradation deposits on MOF surfaces and cross-links to form a hydrophobic PDMS layer (~10 nm). This layer blocks water molecule access to MOF frameworks (reducing water sorption and slowing kinetics) while remaining permeable to substrates (ensuring CO₂ sorption and catalytic site accessibility). XPS and EDS confirm PDMS uniformly coats MOF exteriors without pore blockage.
 Outlook:
Outlook:
This research provides a facile, general strategy to enhance MOF moisture/water stability while preserving porosity—addressing a critical limitation of MOFs. It expands MOF applicability in humid environments (e.g., postcombustion CO₂ capture, heterogeneous catalysis) and sets a benchmark for MOF surface modification.
A Facile and General Coating Approach to Moisture/Water-Resistant Metal−Organic Frameworks with Intact Porosity
Authors: Wang Zhang, Yingli Hu, Jin Ge, Hai-Long Jiang, Shu-Hong Yu
DOI: 10.1021/ja509960n
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja509960n
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.

