Home >
News > Water-Based Synthesis of a Stable Iron-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Capturing Toxic Gases
Water-Based Synthesis of a Stable Iron-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Capturing Toxic Gases
Summary:
The authors from Northwestern University developed Fe-soc-MOF (PCN-250-Fe, Fe-MIL-127) via a water-based synthesis; this highly porous, stable iron-carboxylate MOF exhibits record capacities of 14.7 mmol g⁻¹ NH₃ and 11.7 mmol g⁻¹ SO₂ at 298 K, enabling efficient toxic-gas capture from flue gas.
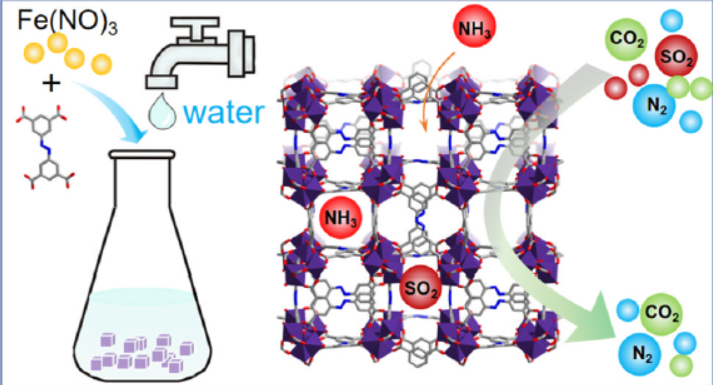
Background:
1. Traditional MOF syntheses use toxic DMF solvents, limiting scale-up; earlier sorbents showed good NH₃/SO₂ uptake but required costly or hazardous routes.
2. The authors proposed a safe, low-cost, aqueous route to Fe-soc-MOF and demonstrated gram-scale production while maintaining porosity and performance.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis
Fe(NO₃)₃·9H₂O + H₄ABTC (3,3′,5,5′-azobenzenetetracarboxylic acid) were heated at 80–95 °C in H₂O with acetic acid modulator; yields 50–60 %, easily scaled to >1 g.
2. Characterizations
1) BET surface area 1470 m² g⁻¹; total pore volume 0.58 cm³ g⁻¹.
2) SEM: crystallites ~100–500 nm.
3) TGA: stable to ~400 °C; PXRD confirms phase purity; NH₃-DRIFTS shows Lewis-acid binding to open Fe sites.
3. Application
Single-component isotherms: 14.7 mmol g⁻¹ NH₃, 11.7 mmol g⁻¹ SO₂ (1 bar, 298 K); IAST selectivity SO₂/CO₂ ≈ 32 and SO₂/N₂ ≈ 575; three-cycle tests retain crystallinity and >75 % capacity.
4. Mechanism
Open Fe(III) nodes act as strong Lewis-acid sites; cooperative guest–guest interactions inside confined pores raise Qst (SO₂) from 26 to 41 kJ mol⁻¹, explaining high uptake and selectivity.
Outlook:
This work delivers a scalable, green synthesis of Fe-soc-MOF for NH₃/SO₂ removal, setting a benchmark for low-cost, high-performance MOF sorbents in environmental remediation.
Water-Based Synthesis of a Stable Iron-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Capturing Toxic Gases
Authors: Zhijie Chen, Xingjie Wang, Ran Cao, Karam B. Idrees, Xinyao Liu, Megan C. Wasson, Omar K. Farha
DOI: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.0c00264
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsmaterialslett.0c00264
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.
