Home >
News > Accelerated photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant over metal-organic framework MIL-53(Fe) under visible LED light mediated by persulfate
Accelerated photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant over metal-organic framework MIL-53(Fe) under visible LED light mediated by persulfate
Summary:
The authors from Department of Environmental Engineering, Wuhan University and Shenzhen Research Institute of Wuhan University developed MIL-53(Fe), a visible-light-responsive metal-organic framework with rod-like structure, good crystallinity, and visible light absorption capacity, achieving efficient photocatalytic degradation of Acid Orange 7 (AO7) under visible LED light mediated by persulfate.
Background:
1. Photocatalysis using solar energy is advantageous for eliminating organic pollutants, but existing MOFs have unsatisfactory efficiency due to fast electron-hole recombination. Previous attempts with oxidants had issues like instability or high dosage.
2. The authors synthesized MIL-53(Fe) and introduced persulfate (PS) to suppress charge carrier recombination, significantly accelerating AO7 degradation under visible LED light.
Research Content:
1. Synthesis:
The authors synthesized MIL-53(Fe) via a solvothermal method. FeCl₃·6H₂O, 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (H₂BDC), and DMF (molar ratio 1:1:280) were reacted at 150°C for 15 h, followed by purification and drying.
2. Characterizations:
1) BET and pore size distribution: Not explicitly provided in the main text.
2) SEM tests: MIL-53(Fe) has a rod-like structure with microrods of 4–10 μm in width and tens of micrometers in length.
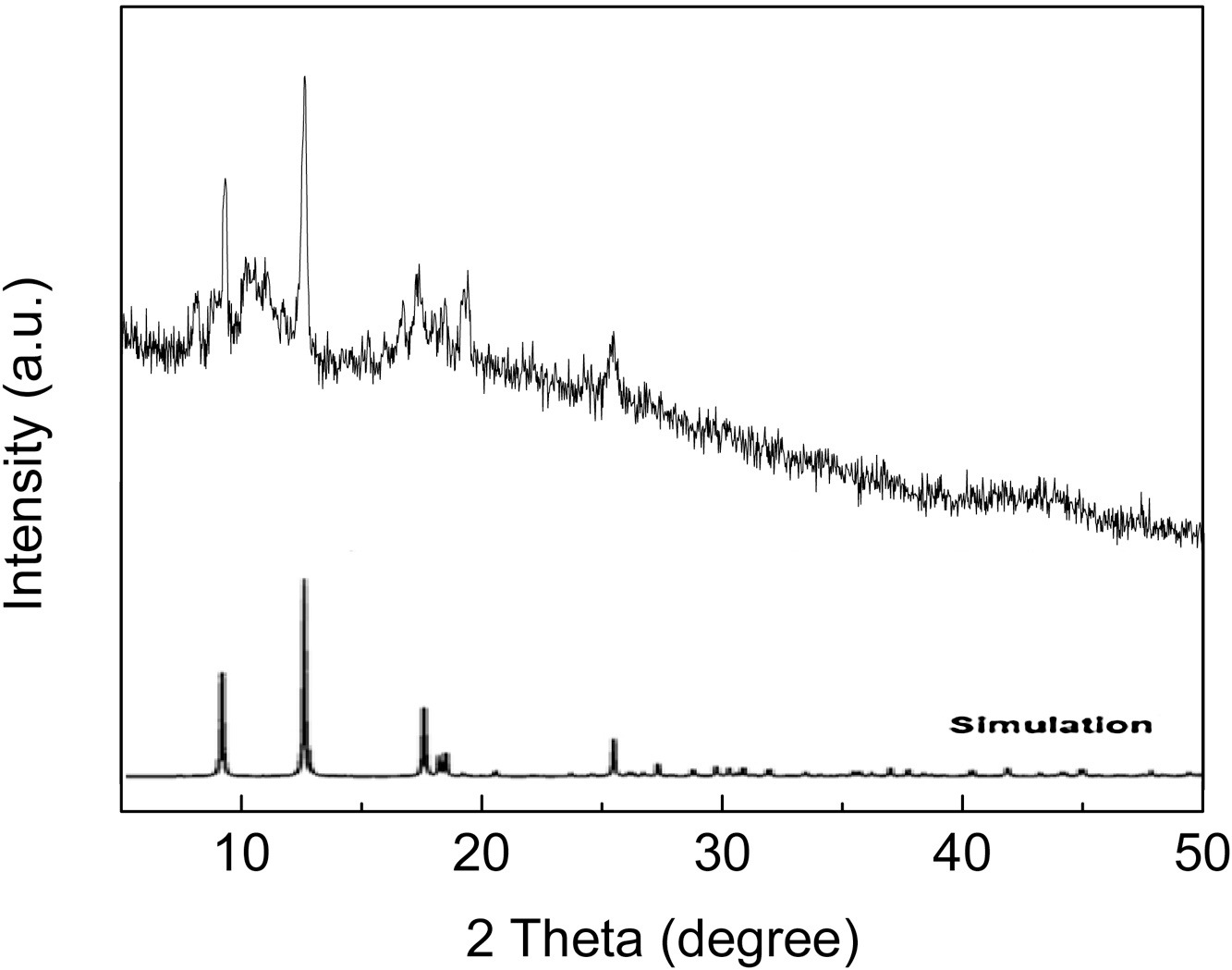
3) Other tests: XRD confirmed crystallinity matching simulated MIL-53(Fe); FTIR showed characteristic peaks of carboxyl groups and Fe–O bonds; XPS identified C, O, Fe elements with Fe(III) in the structure; UV–vis DRS revealed visible light absorption with a band gap of 2.62 eV.
3. Application:
The material was tested for AO7 degradation. In the MIL-53(Fe)/PS/Vis process, AO7 degradation reached ~100% within 90 min, compared to 24% without PS. It showed good reusability over 5 cycles and low iron leaching (~0.37 mg/L) at pH 6.0.
4. Mechanism:
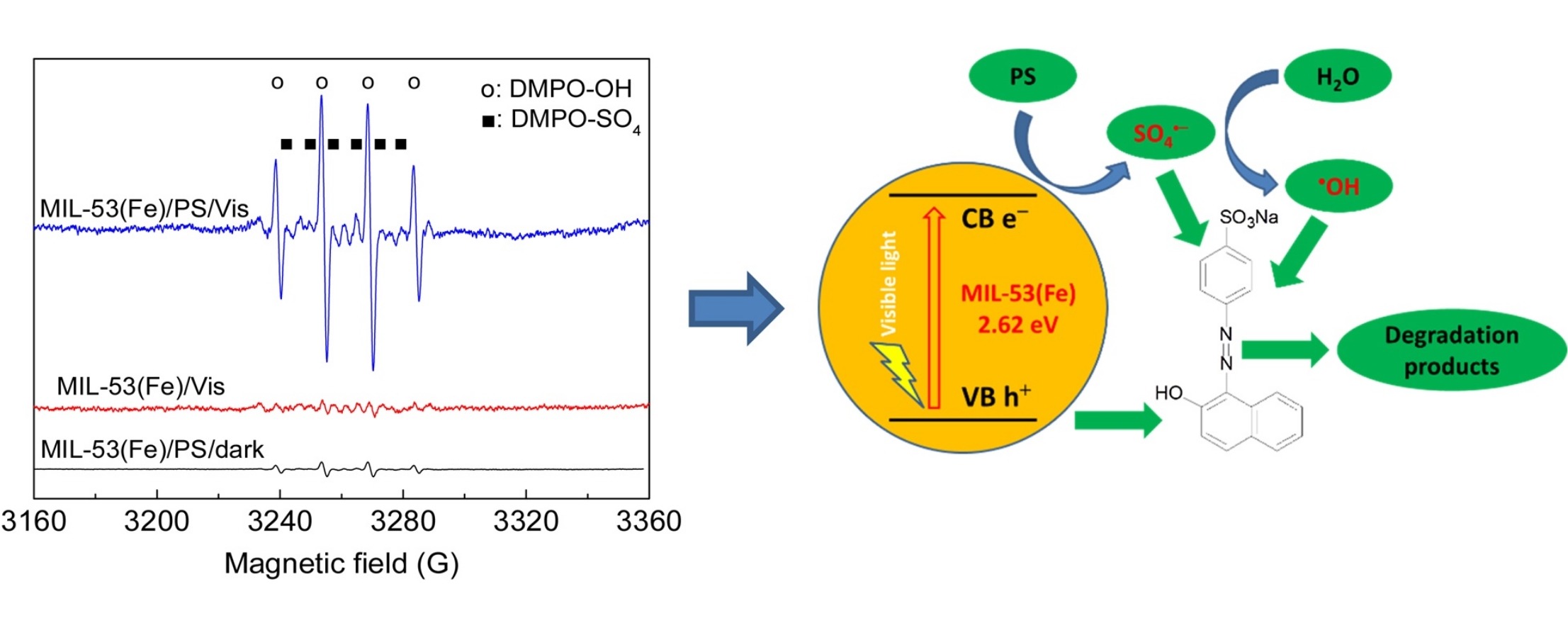
Visible light excites MIL-53(Fe) to generate electrons and holes. PS acts as an electron acceptor, trapping electrons to form SO₄⁻ radicals, suppressing recombination. Holes directly oxidize AO7, and SO₄⁻ converts to ·OH, both accelerating degradation (confirmed by EPR, PL, and electrochemical tests).

Outlook:
This research demonstrates MIL-53(Fe) as a promising photocatalyst in PS-mediated systems for pollutant degradation, offering a cost-effective and efficient approach for wastewater treatment under visible light.
Accelerated photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant over metal-organic framework MIL-53(Fe) under visible LED light mediated by persulfate
Authors: Yaowen Gao, Simiao Li, Yixi Li, Linyu Yao, Hui Zhang
DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.005
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337316306774
The above review is for academic progress sharing. For any errors or copyright issues, please contact us for correction or removal.


